A nurse is assisting with the care of a school-age child who has shigella. Which of the following actions should the nurse take?
Maintain oral rehydration therapy.
Provide a diet high in sodium.
Administer antiviral medication.
Give antidiarrheal agents every 4 hours.
The Correct Answer is A
Choice A rationale:
Maintaining oral rehydration therapy is a crucial nursing action when caring for a child with shigella, which is a bacterial infection that causes severe diarrhea. Oral rehydration therapy helps prevent dehydration and electrolyte imbalances caused by fluid loss from diarrhea. It involves giving the child oral rehydration solutions containing electrolytes and fluids to replace those lost through diarrhea.
Choice B rationale:
Providing a diet high in sodium is not recommended for a child with shigella. Shigella is associated with diarrhea and gastrointestinal symptoms, and a high-sodium diet can worsen fluid imbalances and dehydration.
Choice C rationale:
Shigella is a bacterial infection, not a viral infection, so administering antiviral medication would not be effective or appropriate. Antiviral medications are used to treat viral infections, not bacterial ones like shigella.
Choice D rationale:
Giving antidiarrheal agents every 4 hours is not recommended for a child with shigella. Antidiarrheal agents can slow down the gastrointestinal tract and inhibit the body's natural mechanism for expelling harmful substances, such as bacteria. It's important to allow the body to eliminate the bacteria and toxins causing the infection through diarrhea, while simultaneously providing rehydration support.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Answer: d. Apply suction in 3 to 4-second increments.
Rationale:
- a. Instill 2 mL of 0.9% sodium chloride prior to suctioning:While saline instillations may be used in some cases,it is not universally recommended for infants with tracheostomies and depends on the specific situation and healthcare provider's protocol.The priority in this case is to quickly clear the partial mucus occlusion to prevent respiratory distress.
- b. Select a catheter that fits snugly into the tracheostomy tube:This isincorrect.Selecting a catheter that fits tightly can damage the delicate tracheal mucosa and increase the risk of bleeding.A smaller-diameter catheter that allows for gentle passage is preferred.
Opens in a new window
www.researchgate.net
Tracheostomy tube and different catheter sizes
- c. Use a clean technique when performing suctioning:This is absolutely essential for all suctioning procedures to minimize the risk of infection.However,it is not the specific action that addresses the immediate concern of clearing the partial mucus occlusion.
- d. Apply suction in 3 to 4-second increments:This is thecorrectapproach for suctioning an infant with a tracheostomy.Applying short,intermittent suction bursts minimizes the risk of hypoxia and tissue trauma while effectively removing secretions.
Therefore, the most important action for the nurse to take is to apply suction in short, 3-4 second bursts to effectively clear the mucus occlusion while minimizing risks to the infant.
Additional Points:
- The nurse should use sterile suction equipment and sterile technique throughout the procedure.
- The suction pressure should be set at the lowest effective level,typically 80-120 mmHg.
- The nurse should monitor the infant for signs of respiratory distress,such as increased work of breathing,retractions,and oxygen desaturation,before,during,and after suctioning.
- If the mucus occlusion is not cleared after several attempts,the nurse should seek assistance from ahealthcareprovider.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
Encouraging active range of motion of the extremity is not recommended during the first 12 to 24 hours after a sprained wrist. Early movement can potentially worsen the swelling and delay the healing process.
Choice B rationale:
Applying warm compresses to the extremity is not the best choice to minimize swelling in the initial 12 to 24 hours after a sprained wrist. Heat can actually increase blood flow and promote more swelling in the injured area.
Choice C rationale:
Elevating the extremity above the level of the heart is the correct choice for minimizing swelling in the first 12 to 24 hours after a sprained wrist. Elevating the injured area helps to reduce blood flow to the area, which in turn decreases swelling and promotes healing.
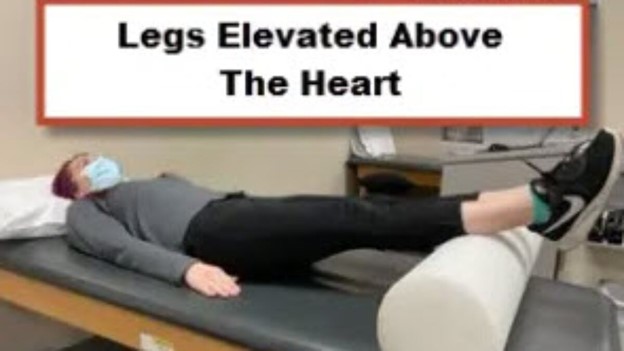
Choice D rationale:
Wrapping the extremity loosely with an elastic bandage might be beneficial for providing support, but it's not the primary intervention for minimizing swelling in the first 12 to 24 hours after a sprained wrist. Elevation is more effective for reducing swelling during this initial period.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
