A nurse at a walk in mental health clinic is assessing a client experiencing severe anxiety. The nurse should recognize the client might exhibit which of the following manifestations?
Attention-seeking conduct
Wild fidgeting
Threatening behavior
Mild difficulty problem solving
The Correct Answer is B
A. In the context of severe anxiety, clients might engage in attention-seeking behaviors as a way to express their distress or seek support. However, wild fidgeting remains a more direct and common manifestation of severe anxiety.
B. Severe anxiety can lead to various physical and psychological manifestations. "Wild fidgeting" is a common physical manifestation of severe anxiety. It involves restlessness, rapid movements, and an inability to sit still. Fidgeting can be a way for individuals to release excess energy and manage their heightened anxiety levels.
C.While severe anxiety can lead to a variety of behaviors, threatening behavior is not a typical or direct manifestation of severe anxiety. Such behavior may be more indicative of other mental health issues or agitation.
D. Severe anxiety is more likely to cause impairments in concentration, focus, and problem-solving abilities rather than mild difficulty. Severe anxiety can lead to cognitive overload and make it challenging for individuals to think clearly and solve problems effectively.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
A) Decreased display of emotions:
While changes in emotional expression can occur in individuals with dementia, it's not a primary manifestation that is typically emphasized when educating families. Behavioral and psychological symptoms, including changes in emotion and personality, can be seen in dementia, but forgetfulness progressing to disorientation is a more direct and characteristic symptom of the condition.
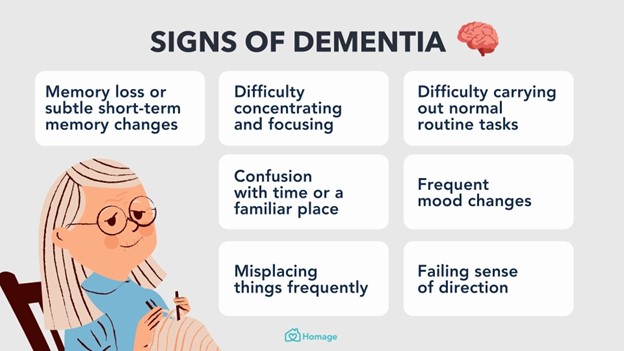
B) Forgetfulness gradually progressing to disorientation
Explanation:
When educating the family of a client with dementia, the nurse should inform them to expect forgetfulness that gradually progresses to disorientation. Dementia is a progressive cognitive decline that affects memory, thinking, and reasoning. Forgetfulness is often one of the initial symptoms of dementia, and as the condition advances, individuals can become disoriented to time, place, and even people. This progression occurs due to the degeneration of brain cells and the accumulation of abnormal proteins.
C) Personality traits that are opposite of original traits:
Changes in personality traits can indeed occur as a result of dementia, but this may not be the most prominent or early manifestation that the nurse would want to highlight when educating the family. The gradual progression of forgetfulness leading to disorientation is a more specific and foundational aspect of dementia.
D) Decreased auditory and visual acuity:
Decreased sensory acuity, such as auditory and visual acuity, can happen with age and various health conditions, but they are not primary manifestations of dementia. Dementia primarily affects cognitive functions like memory, thinking, and reasoning.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
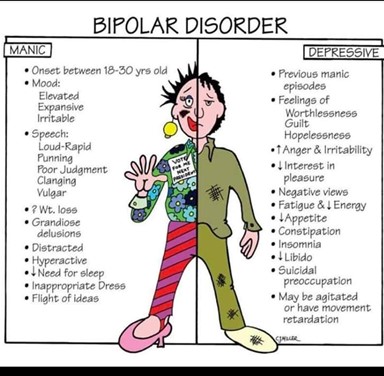
A. The client responds to questions with disorganized speech:
Disorganized speech is a hallmark of acute mania, often reflecting racing thoughts, pressured speech, and difficulty staying on topic.
B. The client reports that voices are telling him to write a novel:
Reporting that voices are telling the client to write a novel suggests auditory hallucinations, which can occur in various psychiatric conditions, not specifically indicative of acute mania.
C. The client's spouse reports that the client has recently gained weight:
Weight gain is not a typical hallmark of acute mania. In fact, during manic episodes, individuals might experience decreased appetite and sleep, leading to potential weight loss.
D. The client is dressed in all black:
Dressing in all black is not a specific sign of acute mania. While changes in clothing choices or appearance can sometimes be associated with mood changes, this finding alone is not indicative of acute mania.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
