A middle-aged school teacher complains of excessive tearing of the eyes every morning. Which assessment should the nurse perform next?
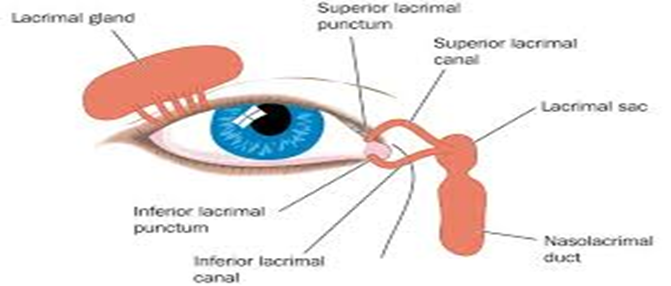
Assess the nasolacrimal sac
Inspect the palpebral conjunctiva
Test pupillary reaction to light
Perform the eye positions test
The Correct Answer is A
Choice A Reason:
The nasolacrimal sac is part of the tear drainage system. When a patient presents with excessive tearing, known as epiphora, it is important to assess for any obstruction in the lacrimal apparatus. The nasolacrimal sac can become blocked due to various reasons such as infection, inflammation, or structural abnormalities. Assessing this area can help determine if there is a blockage causing the tears to accumulate and overflow.
Choice B Reason:
Inspecting the palpebral conjunctiva is typically done if there is a complaint of eye pain or a sensation of a foreign body in the eye. While it is part of a comprehensive eye examination, it is not the first assessment to be performed for excessive tearing unless there are additional symptoms that suggest a problem with the conjunctiva.
Choice C Reason:
Testing the pupillary reaction to light is an assessment of the pupillary response and the function of the oculomotor nerve. This test is crucial when neurological issues are suspected or if there is a change in vision. However, it is not the primary assessment for excessive tearing without other associated symptoms.
Choice D Reason:
The eye positions test, which assesses eye muscle strength and cranial nerve function, is not necessary unless there are signs of problems with muscle strength, such as drooping. This test would not typically be the next step in assessing a patient with excessive tearing unless there are other indications of muscle or nerve impairment.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Choice A Reason:
Rhinitis medicamentosa, also known as rebound congestion, is a condition of nasal congestion without other cold or allergy symptoms, typically caused by the overuse of nasal decongestant sprays. It does not usually present with chronic headaches or tenderness over the sinuses, which are more indicative of sinusitis.
Choice B Reason:
Acute bacterial sinusitis is likely the correct diagnosis in this scenario. It often follows a viral upper respiratory infection and presents with symptoms such as thick, discolored nasal mucus, decreased sense of smell, and facial pain or tenderness over the affected sinuses. The chronic headache and noted tenderness upon palpation over the sinuses in the client are consistent with this condition.
Choice C Reason:
Epistaxis, or nosebleed, is bleeding from the nose that can be caused by various factors, including trauma, medication, or environmental conditions. While it can be a symptom of other nasal conditions, it is not typically associated with chronic headaches or sinus tenderness following an upper respiratory infection.
Choice D Reason:
Allergic rhinitis is an allergic reaction to allergens such as pollen, dust, or pet dander, causing symptoms like sneezing, runny nose, itchy eyes, and sometimes headaches. However, the chronic headache and sinus tenderness described by the client after an infection are more suggestive of sinusitis rather than allergic rhinitis.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Choice A reason:
The primary purpose of health assessment is to collect, analyze, and interpret data to identify the patient’s health status and needs, as well as to develop and implement appropriate nursing interventions to address these needs. It is a systematic process that is fundamental in promoting the health and well-being of patients. This involves a comprehensive evaluation of the patient's physical, psychological, and social health. Gathering this information is crucial for creating a care plan that addresses the individual needs of the client.
Choice B reason:
While health assessments can aid physicians in diagnosing illness, they are not solely for the purpose of diagnosis without further testing. Health assessments may indicate the need for additional tests to confirm a diagnosis. The nurse's role includes supporting the diagnostic process, but it is not the primary purpose of health assessment.
Choice C reason:
Health assessments are not meant to be subjective or based on the nurse's personal views and beliefs. The assessments are conducted to objectively determine the health status of a client, which then informs evidence-based practice and care planning. Personal biases should not influence the management of a client's illness.
Choice D reason:
Making judgments about a client's lifestyle and behaviors is not the primary purpose of health assessment. While lifestyle and behaviors may be assessed as part of understanding the client's overall health status, the goal is not to judge but to understand how these factors may impact the client's health and to provide education and support for healthy changes if needed.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
