A dentist informs the practical nurse (PN) that she has a family history of cancer and has increased the amount of dairy products in her diet to reduce the risk of gingivitis. How should the PN respond?
Suggest an increase in fruits and vegetables is more beneficial.
Encourage the client to get plenty of exercise as well as the dietary change.
Remind the client to make sure the dairy products are fortified with Vitamin D.
Provide written information about the warning signs of cancer.
Provide written information about the warning signs of cancer.
The Correct Answer is A
In this scenario, the dentist is increasing the amount of dairy products in her diet with the aim of reducing the risk of gingivitis due to her family history of cancer. However, the practical nurse (PN) should respond by suggesting that an increase in fruits and vegetables would be more beneficial.
Fruits and vegetables are rich in essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, which can help support overall oral health and reduce the risk of gingivitis. They provide a wide range of nutrients that are important for maintaining healthy gums and teeth.
While dairy products can contribute to overall dental health due to their calcium content, they should not be solely relied upon as the primary means of preventing gingivitis or reducing the risk of cancer. A well- rounded and balanced diet, including plenty of fruits and vegetables, is essential for optimal oral health.
Options b, c, and d are not directly related to the dentist's concern about gingivitis and the increased consumption of dairy products. Encouraging exercise (option b) is generally beneficial for overall health, but it does not specifically address gingivitis. Reminding the client to ensure dairy products are fortified with vitamin D (option c) is not necessary in this context, as the focus is on preventing gingivitis rather than addressing vitamin D deficiency. Providing written information about the warning signs of cancer (option d) is not directly relevant to the dentist's current situation and concern about gingivitis.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is ["A","D","E"]
Explanation
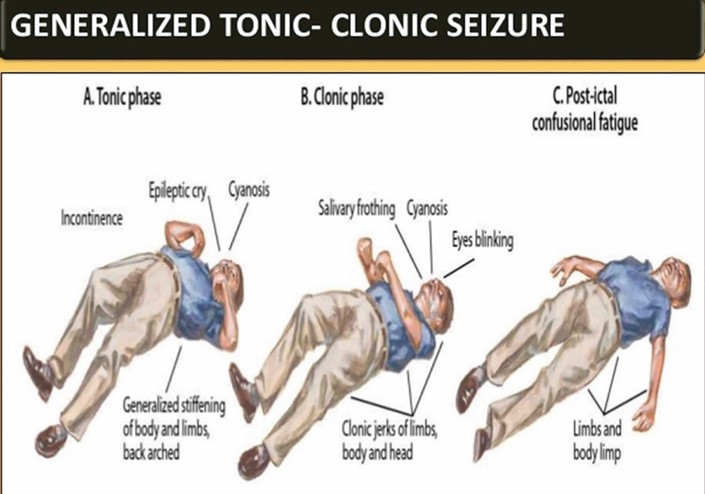
During a generalized tonic-clonic seizure, it is important for the practical nurse (PN) to prioritize the safety and well-being of the child. The correct actions to implement immediately are:
A. Observe the progression of the seizure: The PN should closely observe the seizure to gather important information that can be helpful for medical professionals in assessing the seizure's characteristics and duration.
D. Pad the side rails with pillows: Padding the side rails of the bed with pillows helps to prevent the child from injuring themselves by hitting the side rails during the seizure.
E. Loosen clothing around the neck: Loosening any tight clothing around the child's neck helps to ensure adequate breathing and prevent any constriction or discomfort during the seizure.
B. Hold the extremities close to the body: This action is not recommended during a seizure as it may increase the risk of injury to the child or the PN.
C. Insert a tongue blade between the teeth: It is not recommended to insert any object, including a tongue blade, between the teeth of a person experiencing a seizure. This can cause injury to the person's mouth or teeth and is no longer considered an appropriate intervention for seizures.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
- Medication administration is a process that involves prescribing, dispensing, and giving medications to patients. It is a critical and complex task that requires accuracy, safety, and adherence to the rights of medication administration, such as the right patient, right drug, right dose, right route, right time, right documentation, and right response.
- When a male client tells the practical nurse (PN) that the pill he has been taking at home is a different color and size than the one the PN is trying to give him now, this may indicate a potential medication error
or discrepancy. A medication error is any preventable event that may cause or lead to inappropriate medication use or patient harm. A medication discrepancy is any difference between the current and previous medication regimens of a patient.
- The PN should respond to the client's concern by telling him that the PN will verify that the dispensed medication is a valid prescription. This means that the PN will check the medication label, the medication order, and the medication administration record (MAR) to confirm that the medication given to the client matches the one prescribed by the healthcare provider. The PN will also compare the dispensed medication with a drug reference guide or a picture of the medication to ensure that it is the correct drug and dosage form. The PN will also report any suspected errors or discrepancies to the healthcare provider or the pharmacy for clarification or correction.
- Options A, B, and D are incorrect answers, as they do not reflect the appropriate or responsible actions for the PN to take when faced with a possible medication error or discrepancy.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
