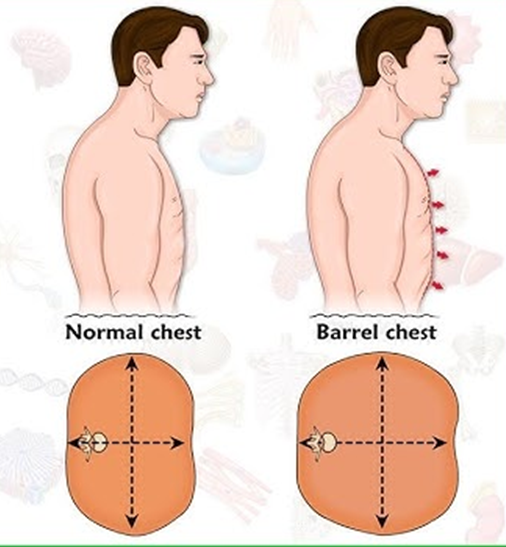
While examining a client, the nurse observes the client's chest to be barrel-shaped. The nurse would interpret this as indicating which of the following?
Pigeon Chest
Pneumonia
Funnel Chest
COPD
The Correct Answer is D
Choice a reason:
Pigeon Chest, or pectus carinatum, is a condition where the breastbone is pushed outward, and the chest appears to protrude. It is not typically associated with a barrel-shaped chest, which is characterized by a rounded and bulging appearance.
Choice b reason:
Pneumonia is an infection that inflames the air sacs in one or both lungs, which may fill with fluid or pus. While it can cause chest expansion, it does not lead to a barrel-shaped chest. The barrel-shaped chest is more indicative of a chronic condition rather than an acute infection like pneumonia.
Choice c reason:
Funnel Chest, or pectus excavatum, is a condition where the breastbone is sunken into the chest. Unlike a barrel-shaped chest, funnel chest gives the chest a depressed appearance.
Choice d reason:
COPD, or Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease, is commonly associated with a barrel-shaped chest. This shape results from the chronic hyperinflation of the lungs due to obstructive lung disease, which causes the rib cage to remain expanded.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Choice A Reason:
Vertigo is a common complication associated with inner ear infections, such as labyrinthitis or vestibular neuritis. The inner ear is responsible for balance, and when it is infected, it can lead to a sensation of spinning or dizziness. Interventions may include medications like meclizine or dimenhydrinate to alleviate symptoms, as well as safety measures to prevent falls.
Choice B Reason:
Rhinorrhea, or a runny nose, is not typically a direct complication of an inner ear infection. It may be associated with upper respiratory infections that can precede or accompany an ear infection but is not a result of the inner ear infection itself.
Choice C Reason:
Fever may be present if the inner ear infection is part of a systemic infection, such as the flu or bacterial meningitis. However, fever is not a direct result of an isolated inner ear infection. If fever is present, the nurse should monitor the patient's temperature and may administer antipyretics as ordered.
Choice D Reason:
Headache can be a symptom experienced by individuals with inner ear infections due to the general discomfort and pressure changes in the ear. However, it is not as specific or as common as vertigo when it comes to inner ear infections. If headaches are present, pain management strategies can be included in the care plan.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Choice A reason:
Acute pain is typically sudden in onset and is usually the result of a specific injury or illness. It is characterized by its sharp quality and tends to last for a short duration, generally not longer than six months. Since the patient's knee pain has persisted for eleven months, it does not fall under the category of acute pain.
Choice B reason:
Intermittent pain is pain that comes and goes at intervals. Although the patient's pain could be intermittent, the classification based on duration would not be described as intermittent. This term refers more to the pattern of the pain rather than its chronicity or cause.
Choice C reason:
Chronic pain is defined as pain that persists for longer than six months, often continuing even after the injury or illness that caused it has healed. The patient's bilateral knee pain has been present for eleven months, which exceeds the six-month threshold, thus categorizing it as chronic pain.
Choice D reason:
Idiopathic pain refers to pain that arises without a clear cause. It is not categorized based on the duration of the pain but rather on the absence of an identifiable underlying reason. Since the patient's pain has a specific duration, it is not appropriate to classify it as idiopathic without further information regarding its cause.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
