The nurse is caring for a client with an acute myocardial infarction (AMI). What emergent procedure does the nurse anticipate the physician will order?
Exercise electrocardiography.
Computed tomography (CT) of the chest with contrast.
Echocardiogram.
Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI).
The Correct Answer is D
Choice A rationale
Exercise electrocardiography, also known as a stress test, is not typically the first-line emergent procedure for a patient with an acute myocardial infarction (AMI). This test is often used to diagnose coronary artery disease, but it is not typically used to treat an AMI5.
Choice B rationale
A computed tomography (CT) scan of the chest with contrast could be used to visualize the heart and surrounding structures, but it is not typically the first-line emergent procedure for a patient with an AMI5.
Choice C rationale
An echocardiogram could be used to visualize the heart’s structure and function, but it is not typically the first-line emergent procedure for a patient with an AMI5.
Choice D rationale
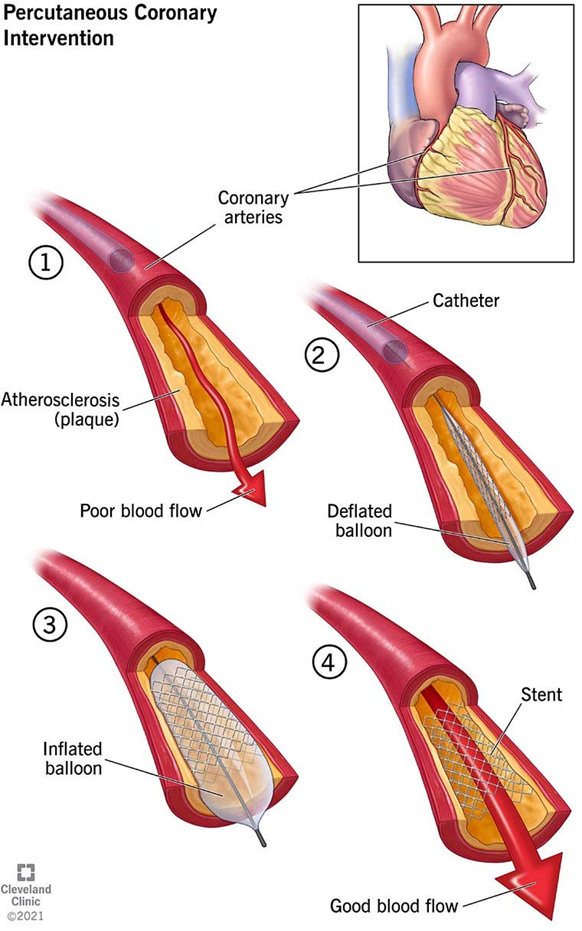
Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) is the correct answer. This procedure is often used as an emergent treatment for an AMI. It involves using a catheter to place a small structure called a stent to open up blood vessels in the heart that have been narrowed by plaque buildup.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Choice A rationale
Beginning cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is not the first action a nurse should take when a patient’s heart monitor shows a pattern of undulations of varying contours and amplitude with no measurable ECG pattern.
Choice B rationale
Cardioverting the client with a biphasic defibrillator is not the first action a nurse should take when a patient’s heart monitor shows a pattern of undulations of varying contours and amplitude with no measurable ECG pattern.
Choice C rationale
The first action a nurse should take when a patient’s heart monitor shows a pattern of undulations of varying contours and amplitude with no measurable ECG pattern is to assess the patient’s airway, breathing, and circulation.
Choice D rationale
Administering an amiodarone bolus followed by a drip is not the first action a nurse should take when a patient’s heart monitor shows a pattern of undulations of varying contours and amplitude with no measurable ECG pattern.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Choice A rationale
A pleural friction rub is an audible raspy breathing sound, a medical sign present in some patients with pleurisy and other conditions affecting the chest cavity. It is not a typical symptom of cardiac tamponade.
Choice B rationale
Distended neck veins are a result of the collapsed blood vessels that should return blood to the heart. This is a common symptom of cardiac tamponade.
Choice C rationale
Widening pulse pressure occurs with valvular heart disease, not typically with cardiac tamponade.
Choice D rationale
Bradycardia, or a slower-than-normal heart rate, is not typically associated with cardiac tamponade.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
