A patient with diabetic ketoacidosis is brought to the emergency department. Which prescribed action should the nurse implement first?
Bring the patient a meal.
Administer Lantus insulin IV.
Give sodium bicarbonate 50 mEq IV push.
Start an infusion of normal saline at 125 ml/hr.
The Correct Answer is D
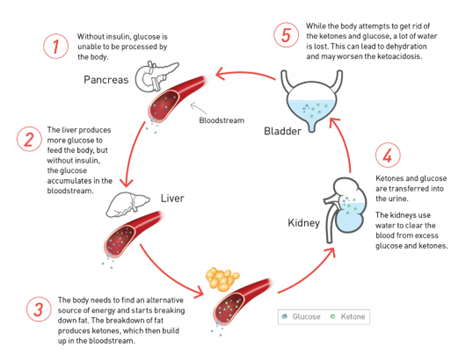
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious complication of diabetes that occurs when the body produces high levels of blood acids called ketones. The initial management of DKA involves fluid resuscitation with intravenous normal saline to correct dehydration and electrolyte imbalances. Therefore, starting an infusion of normal saline at 125 ml/hr is the first prescribed action the nurse should implement.
Bringing the patient a meal is not a priority at this time because the patient's blood glucose levels need to be stabilized before they can safely consume food. Administering Lantus insulin IV and giving sodium bicarbonate 50 mEq IV push are also not the first-line treatments for DKA. Lantus insulin is a long-acting insulin used to treat hyperglycemia over an extended period and should not be given intravenously. Sodium bicarbonate may be used to correct acidosis, but it is not the first priority in DKA management.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Diabetes insipidus is a condition in which the body is unable to properly regulate fluid balance, leading to excessive urination (polyuria) and thirst. Therefore, the nurse should anticipate the clinical manifestation of polyuria in a patient admitted to the hospital with diabetes insipidus. The patient may excrete large amounts of dilute urine, which can lead to dehydration if adequate fluid replacement is not provided. The other options listed (fluid volume overload, decreased gas exchange, and generalized edema) are not typically associated with diabetes insipidus, as this condition is characterized by a deficiency of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) rather than an excess of fluid.

Correct Answer is A
Explanation
The nurse should anticipate that the patient will need to collect a stool specimen. Diarrhea can be caused by various factors such as infections, inflammatory bowel disease, food intolerance, and medication side effects. Collecting a stool specimen can help identify the underlying cause of the diarrhea and guide appropriate treatment. Blood cultures, colonoscopy but barium enema may be necessary in certain cases but are not typically the first step in the diagnostic process for diarrhea.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
