A nurse is conducting preoperative teaching with a client who is to undergo open abdominal surgery. Which of the following is important to prevent postoperative complications?
Discuss pain management with the client.
Explain the need for sequential compression devices.
Review the policy with the client and family.
Ensure the operative site has been secured.
The Correct Answer is B
Choice A reason: Discussing pain management is important for patient comfort but does not directly prevent postoperative complications.
Choice B reason: Sequential compression devices are used to prevent deep vein thrombosis, a common postoperative complication, making this the correct answer.
Choice C reason: Reviewing policy with the client and family is part of the overall care but is not specific to preventing postoperative complications.
Choice D reason: Ensuring the operative site has been secured is a procedural task and does not directly prevent postoperative complications.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
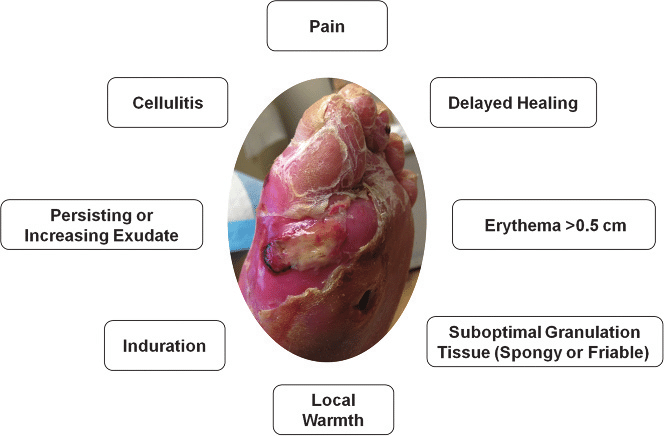
Choice A reason: Swelling and tenderness around a wound are common signs of infection. The body's inflammatory response to the invading bacteria causes these symptoms.
Choice B reason: Serosanguineous drainage, which is composed of both blood and a clear yellow liquid called serum, is typically a normal part of the healing process and not necessarily a sign of infection.
Choice C reason: Bromocriptine is a medication and not a sign of wound infection. This choice seems to be a distractor and does not relate to the clinical signs of a wound infection.
Choice D reason: Urticaria, also known as hives, is a reaction that can be caused by an allergy, stress, or other factors, and is not a direct sign of wound infection.
Correct Answer is ["1"]
Explanation
Step 1: Identify the prescribed dose and the dose per tablet. The prescribed dose is 100 mcg and the dose per tablet is also 100 mcg.
Step 2: Divide the prescribed dose by the dose per tablet to find out how many tablets are needed. So, 100 mcg (prescribed dose) ÷ 100 mcg/tablet (dose per tablet) = 1 tablet
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
