What is the function of the neuromuscular junction?
To connect muscle fibers to motor neurons
To bind acetylcholine to nAChRs
To depolarize the muscle cell membrane.
To activate voltage-gated sodium channels on the muscle membrane .
Correct Answer : A
The neuromuscular junction is a type of synapse where neuronal signals from the brain or spinal cord interact with skeletal muscle fibers, causing them to contract.
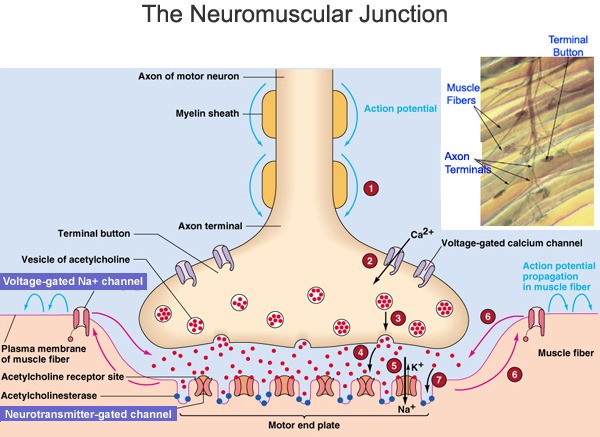
The activation of many muscle fibers together causes muscles to contract, which in turn can produce movement.
Choice B is incorrect because binding acetylcholine to nAChRs is a process that occurs at the neuromuscular junction, but it is not the function of the neuromuscular junction itself.
Choice C is incorrect because depolarizing the muscle cell membrane is a result of the function of the neuromuscular junction, but it is not the function itself.
Choice D is incorrect because activating voltage-gated sodium channels on the muscle membrane is a result of the function of the neuromuscular junction, but it is not the function itself.
TEAS 7 Exam Quiz Bank
HESI A2 Exam Quiz Bank
Find More Questions 📚
Teas 7 Questions: We got the latest updated TEAS 7 questions
100% Money Refund: 100% money back guarantee if you take our full
assessment pass with 80% and fail the actual exam.
Live Tutoring: Fully customized live tutoring lessons.
Guaranteed A Grade: All students who use our services pass with 90%
guarantee.
Related Questions
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
The correct answer is choice A.
The shape and surface area of the object.
The terminal velocity of an object falling through a fluid is affected by several factors, including its mass and shape.
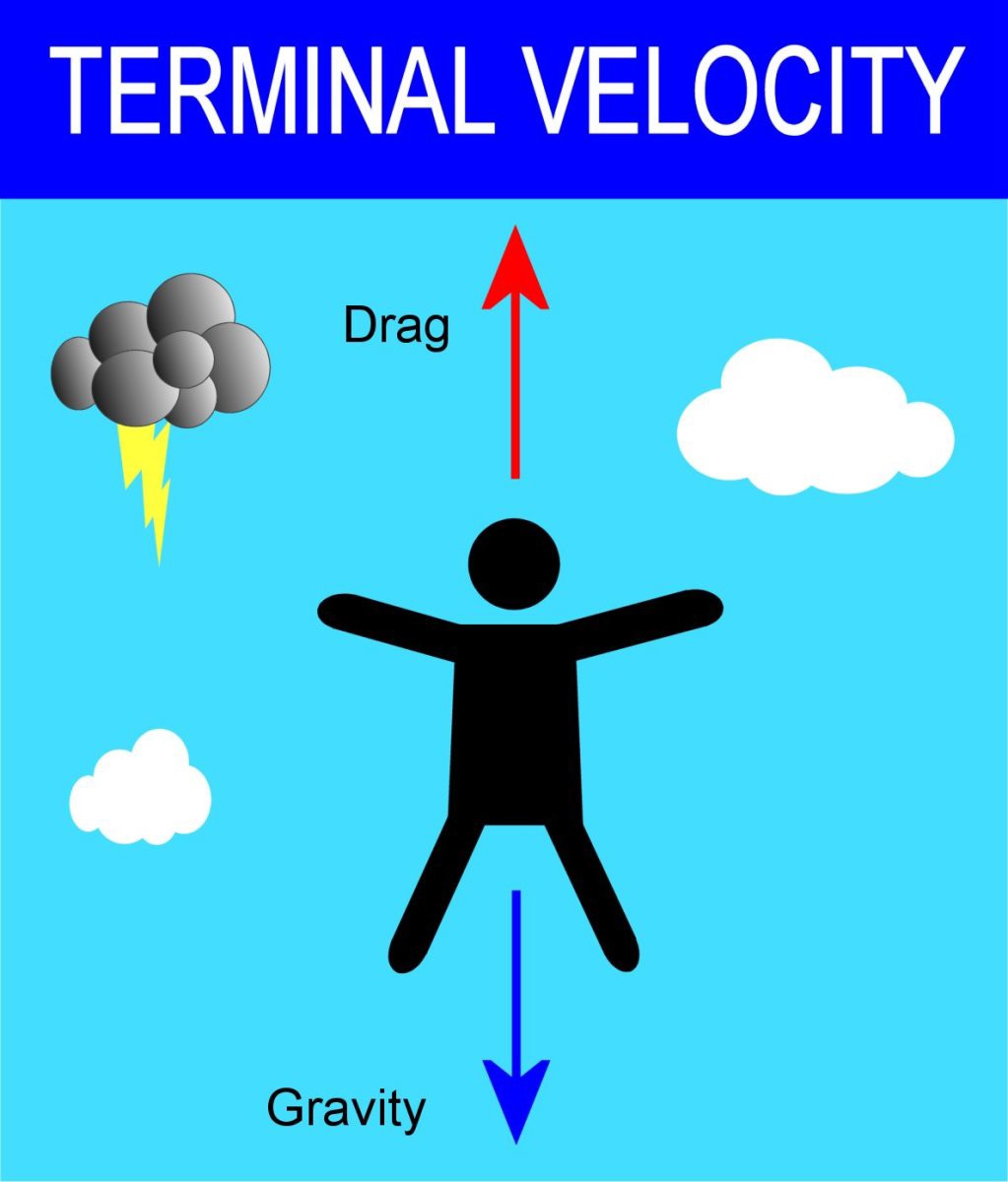
Objects with large surface areas will often experience a large amount of air resistance when they move.
Choice B is incorrect because the volume of the object does not affect its terminal velocity.
Choice C is incorrect because the acceleration and momentum of the object do not affect its terminal velocity.
Choice D is incorrect because the height and distance of the fall do not affect the terminal velocity of a falling object.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
The correct answer is choice C. Substitution.
A substitution mutation is a type of point mutation where one base in the DNA sequence is replaced by another base.
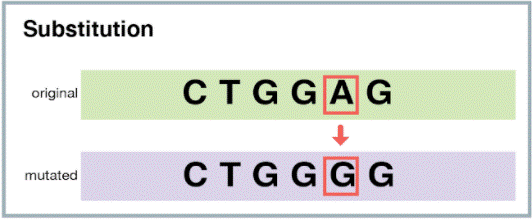 |
Choice A is incorrect because a deletion mutation occurs when one or more bases are removed from the DNA sequence.
Choice B is incorrect because an insertion mutation occurs when one or more bases are added to the DNA sequence.
Choice D is incorrect because an inversion mutation occurs when a segment of DNA is reversed within the chromosome.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
The correct answer is choice A. Hydrogen bonds.
Hydrogen bonds are responsible for the unique properties of water and play a crucial role in the structure of DNA and proteins.
Hydrogen bonds are weak electrostatic attractions between a hydrogen atom covalently bonded to an electronegative atom and another electronegative atom.
Choice B.
Covalent bonds is incorrect because covalent bonds are strong chemical bonds formed by the sharing of electrons between two atoms.
Choice C.
Ionic bonds is incorrect because ionic bonds are chemical bonds formed by the transfer of electrons from one atom to another, resulting in the formation of ions.
Choice D.
Van der Waals forces is incorrect because Van der Waals forces are weak intermolecular forces that arise from temporary dipoles induced in atoms or molecules.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
The correct answer is choice C. Thyroxine.
Thyroxine (T4) is a hormone produced by the thyroid gland that controls your body’s metabolism, the process in which your body transforms the food you eat into energy.
Choice A, Estrogen, is not the correct answer because it is a hormone responsible for the development of female secondary sexual characteristics.
Choice B, Progestin, is not the correct answer because it is a synthetic form of progesterone used in hormonal birth control and hormone replacement therapy.
Choice D, Androgen, is not the correct answer because it is a hormone responsible for the development of male secondary sexual characteristics.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
The correct answer is choice A. Keratin.
Keratin is a fibrous protein that provides strength and protection to the body, particularly in the skin, hair, and nails.
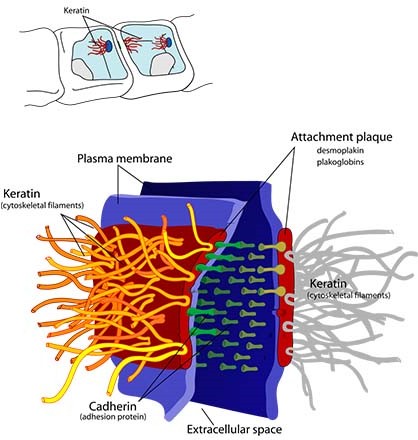 |
It is found in epithelial tissue, which covers the body’s surface and lines its internal organs and cavities.
Choice B.
Collagen is incorrect because collagen is a fibrous protein that provides strength and support to connective tissues such as tendons, ligaments, and cartilage.
Choice C.
Elastin is incorrect because elastin is a protein that provides elasticity to tissues such as skin and blood vessels.
Choice D.
Actin is incorrect because actin is a protein that plays a role in muscle contraction and cell movement.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Bacteria can perform photosynthesis while archaea cannot. Many types of bacteria can generate oxygen from sunlight through photosynthesis, while archaea cannot perform this process.
Choice A is incorrect because neither bacteria nor archaea have a true nucleus. Both are prokaryotic organisms. Choice B is incorrect because archaea reproduce by fission, fragmentation, or budding, while bacteria can produce spores and divide sexually or asexually. Choice D is incorrect because archaeal and bacterial flagella are constructed differently.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Natural killer cells.
Natural killer (NK) cells are large granular lymphocytes that are capable of destroying cells infected by viruses or bacteria and susceptible tumor cells without prior sensitization and restriction by MHC antigens.
Helper T cells (choice A) are a type of white blood cell that helps other immune cells respond to infections but do not directly kill infected or tumor cells.
B cells (choice B) are a type of white blood cell that produces antibodies to fight infections but do not directly kill infected or tumor cells.
Cytotoxic T cells (choice D) are a type of white blood cell that can kill infected or tumor cells but require prior sensitization to do so.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
The correct answer is choice B.
Using a placebo group and a double-blind technique for giving the medications is the best way to ensure that the study is valid and reliable.
A placebo group helps control for the placebo effect, which can influence the results of a study.
A double-blind technique means that neither the patients nor the researchers know which medication is being given, reducing bias.
Choice A is not the best answer because while a large sample size and standardized procedure can increase reliability, they do not address validity.
Choice C is not the best answer because a matched-pairs design and crossover technique are useful for reducing variability but do not address validity.
Choice D is not the best answer because a convenience sample may not be representative and a pretest-posttest design does not control for extraneous variables.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
The correct answer is choice A.
An increase in viscosity of a fluid results in a decrease in mobility of particles.
Viscosity is the resistance of a fluid to a change in shape or movement of neighboring portions relative to one another.
It denotes opposition to flow and may be thought of as internal friction between the molecules.
Choice B is incorrect because an increase in viscosity does not affect the density of a fluid.
Choice C is incorrect because an increase in viscosity results in a decrease, not an increase, in flow rate.
Choice D is incorrect because an increase in viscosity does not affect the pressure of a fluid.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
The correct answer is choice A. Thymus.
The thymus is a primary lymphoid organ located in the mediastinum.
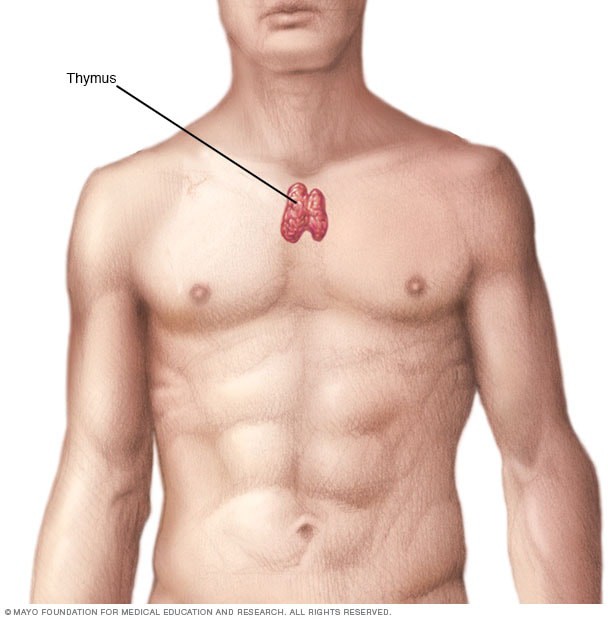 |
It plays a key role in the maturation and differentiation of T-lymphocytes.
Choice B.
Parathyroid is incorrect because the parathyroid glands are small endocrine glands located in the neck that produce parathyroid hormone, which regulates calcium levels in the blood.
Choice C.
Adrenal is incorrect because the adrenal glands are endocrine glands located above the kidneys that produce hormones such as cortisol and adrenaline.
Choice D.
Pituitary is incorrect because the pituitary gland is an endocrine gland located at the base of the brain that produces hormones that regulate growth, metabolism, and reproductive functions.
This question was extracted from the actual TEAS Exam. Ace your TEAS exam with the actual TEAS 7 questions, Start your journey with us today
Visit Naxlex, the Most Trusted TEAS TEST Platform With Guaranteed Pass of 90%.
Money back guarantee if you use our service and fail the actual exam. Option of personalised live tutor on your area of weakness.
