What is the function of ribosomes in a cell?
To produce energy for the cell
To store genetic information
To transport molecules within the cell
To synthesize proteins in the cell
Correct Answer : D
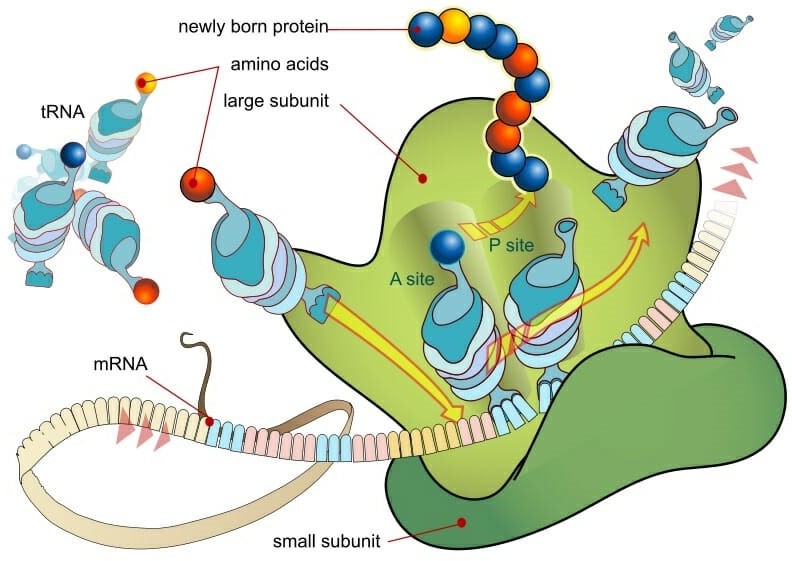
Ribosomes are small, spherical structures found in all living cells, including bacteria, archaea, and eukaryotes. Their primary function is to synthesize proteins using the genetic information stored in the cell's DNA. Ribosomes are composed of two subunits, one large and one small, that come together during protein synthesis.
Ribosomes read the genetic information stored in mRNA (messenger RNA) and use this information to assemble amino acids in the correct order to form a protein. The ribosome moves along the mRNA, adding one amino acid at a time to the growing protein chain until it reaches the end of the mRNA and the protein is complete.
Proteins are essential for a wide variety of cellular functions, including catalyzing chemical reactions, providing structural support, and transporting molecules across cell membranes. Therefore, ribosomes play a critical role in the overall function and survival of a cell.
TEAS 7 Exam Quiz Bank
HESI A2 Exam Quiz Bank
Find More Questions 📚
Teas 7 Questions: We got the latest updated TEAS 7 questions
100% Money Refund: 100% money back guarantee if you take our full
assessment pass with 80% and fail the actual exam.
Live Tutoring: Fully customized live tutoring lessons.
Guaranteed A Grade: All students who use our services pass with 90%
guarantee.
Related Questions
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
A buffer is a solution that resists changes in pH when small amounts of an acid or base are added. Buffers work by neutralizing added hydrogen ions (H⁺) or hydroxide ions (OH⁻), thereby maintaining a relatively stable pH. Buffers are made up of a weak acid and its conjugate base or a weak base and its conjugate acid.
- A. It decreases the pH of the solution: This is incorrect because a buffer does not always decrease pH; it resists changes in both directions.
- C. It causes the pH of a solution to become neutral: Incorrect because buffers do not necessarily make a solution neutral; they stabilize pH around a certain value.
- D. It permanently binds hydrogen ions: Incorrect as the binding is reversible, which is essential for maintaining pH balance.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
The key structural difference between starch and cellulose lies in the type of glucose monomers they contain:
- Starch is composed of alpha-glucose monomers, which are linked by α(1→4) glycosidic bonds.
- Cellulose is composed of beta-glucose monomers, which are linked by β(1→4) glycosidic bonds.
This difference in the orientation of the glucose molecules leads to different structural properties:
- In starch, the alpha-glucose linkage causes the molecules to form a helical, more easily digestible structure.
- In cellulose, the beta-glucose linkage results in straight, rigid chains that form strong fibers through hydrogen bonding, making it difficult for most organisms to digest.
The other options are incorrect:
- A. Incorrect, as cellulose fibrils do have hydrogen bonds, which contribute to its rigid structure.
- B. Incorrect, as both starch and cellulose are made of glucose, not fructose.
- D. Incorrect, both starch and cellulose contain cyclized glucose monomers, but the orientation differs.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
This reaction involves an acid (hydrochloric acid, HCl) and a base (magnesium hydroxide, Mg(OH)₂) reacting to form water (H₂O) and a salt (magnesium chloride, MgCl₂). This is a classic neutralization reaction, where an acid reacts with a base to neutralize each other, producing water and a salt.
- Neutralization Reaction: Acid + Base → Water + Salt
- In this case:
- Acid: HCl (hydrochloric acid)
- Base: Mg(OH)₂ (magnesium hydroxide)
- Products: H₂O (water) and MgCl₂ (magnesium chloride)
The other options do not apply:
- A. Decomposition: A single compound breaks down into two or more substances. Not the case here.
- B. Combustion: A substance reacts with oxygen, often producing heat and light (usually with organic compounds). Not the case here.
- C. Synthesis: Two or more substances combine to form a single product. Not applicable to this reaction.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
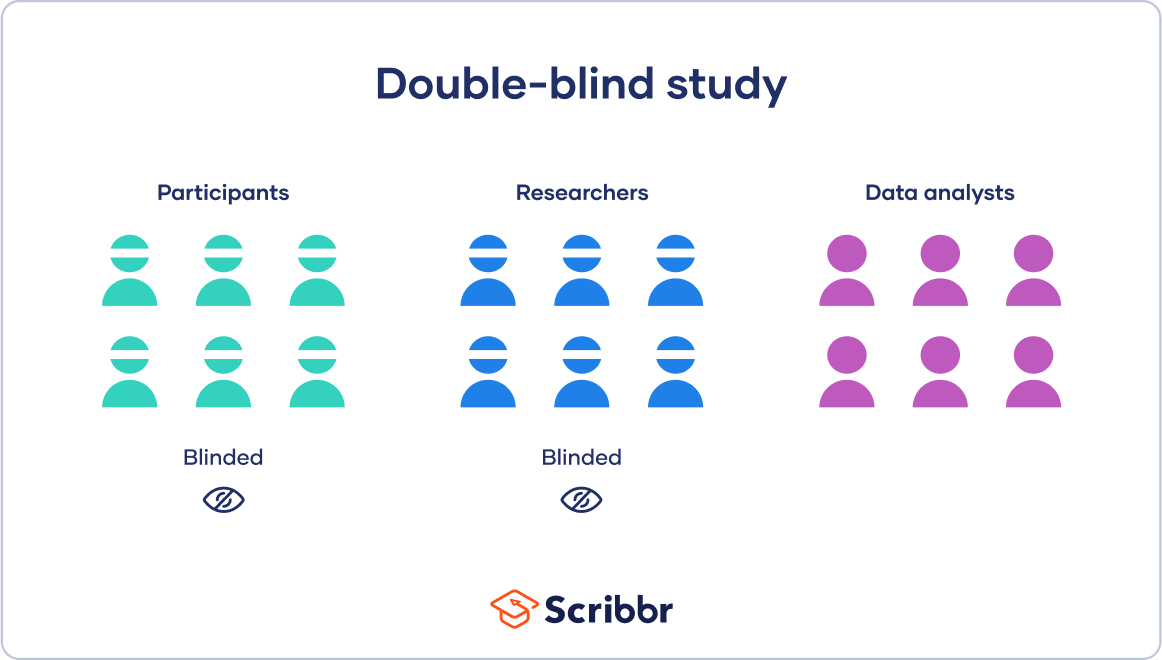
A double-blind study is a research design in which neither the participants nor the researchers know which group participants are assigned to. This is done to minimize bias and ensure that the results of the study are as objective as possible. In a double-blind study, the treatment and control groups are randomly assigned, and the participants and researchers are unaware of which group each participant is assigned to. Option a) is an example of a randomized controlled trial, which is a common research design, but it is not necessarily double-blind. Option b) is an example of an open-label study, in which both the participants and the researchers know which group each participant is assigned to. Option c) is an example of a single-blind study, in which the participants do not know which group they are assigned to, but the researchers do.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
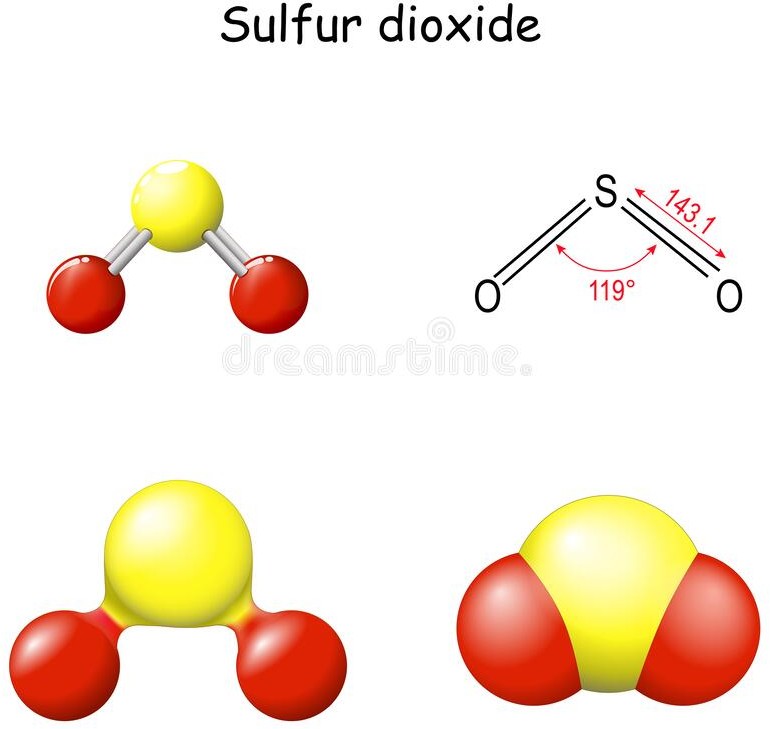
The molecular geometry of a molecule of sulphur dioxide (SO2) is bent or V-shaped. This is because of the presence of two lone pairs on the sulfur atom, which cause repulsion and distort the bond angles in the molecule.
SO2 has a central sulfur atom bonded to two oxygen atoms by double bonds. The two double bonds and the two lone pairs of electrons on sulfur result in a trigonal planar arrangement of electron pairs around the sulfur atom. However, the repulsion between the lone pairs causes the two oxygen atoms to be pulled closer together, resulting in a bent or V-shaped molecular geometry.
The bent molecular geometry of SO2 affects its properties, such as its polarity and reactivity. SO2 is a polar molecule due to the asymmetric distribution of electrons, which results in a partial positive charge on the sulfur atom and partial negative charges on the oxygen atoms. This polarity makes SO2 a good solvent and reactant in chemical reactions, as well as a contributor to air pollution and acid rain.
 |
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
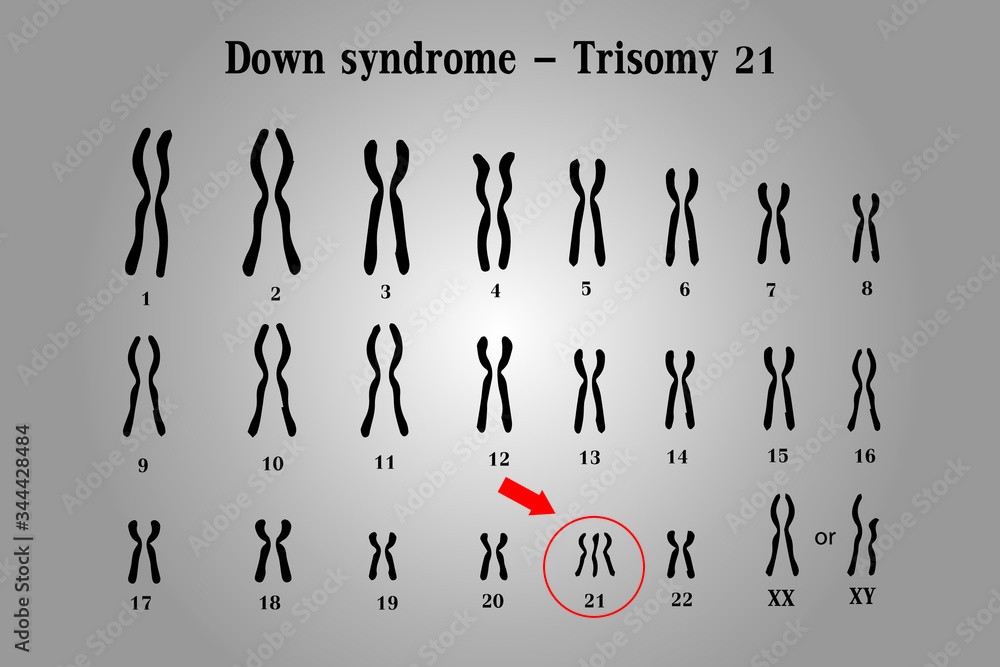
Down syndrome is a genetic disorder caused by the presence of an extra copy of chromosome 21. It is also known as trisomy 21, because affected individuals have three copies of chromosome 21 instead of the normal two.
The extra chromosome 21 in Down syndrome occurs due to a random error in cell division, which leads to the production of an abnormal gamete (egg or sperm) with an extra copy of the chromosome. When this gamete fuses with a normal gamete during fertilization, the resulting zygote has 47 chromosomes instead of the usual 46, and develops into a fetus with Down syndrome.
Down syndrome is characterized by a range of physical and intellectual symptoms, including developmental delays, intellectual disability, distinctive facial features, heart defects, and increased risk of certain medical conditions such as leukemia and Alzheimer's disease. However, the severity and expression of these symptoms can vary widely among affected individuals.
 |
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
The chemical formula for water is H2O. It consists of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom.
 |
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
The mitral valve is located between the left atrium and left ventricle of the heart and helps to regulate the flow of blood between these chambers. It consists of two leaflets or flaps that open and close in response to changes in pressure as the heart beats.
During diastole, when the heart is relaxed and filling with blood, the mitral valve opens to allow blood to flow from the left atrium into the left ventricle. During systole, when the heart contracts to pump blood out of the left ventricle and into the systemic circulation, the mitral valve closes to prevent backflow of blood into the left atrium.
The mitral valve is one of four valves in the heart that help to ensure the unidirectional flow of blood through the heart and the rest of the circulatory system. Problems with the mitral valve, such as mitral valve prolapse or mitral stenosis, can lead to a range of symptoms and complications, including shortness of breath, fatigue, chest pain, and heart failure.
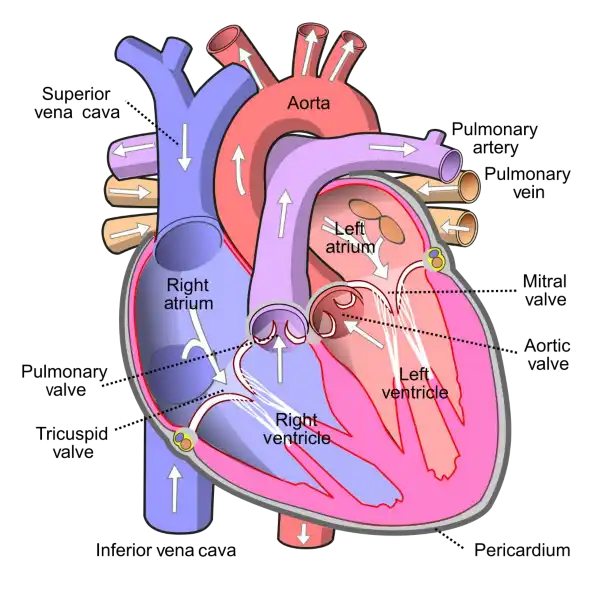 |
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Carbohydrates are one of the main types of biomolecules and are composed of monomers called monosaccharides. Monosaccharides are simple sugars that cannot be further broken down into simpler sugars. They are usually composed of 3 to 7 carbon atoms and have a general formula of (CH2O)n, where n is a number between 3 and 7. Examples of monosaccharides include glucose, fructose, and galactose.
When two monosaccharides are joined together by a glycosidic bond, they form a disaccharide. Disaccharides are composed of two simple sugars and can be broken down into their constituent monosaccharides by hydrolysis. Examples of disaccharides include sucrose, lactose, and maltose.
Option a) is incorrect because it describes the composition of a disaccharide, not a monosaccharide. Option
c) is incorrect because both monosaccharides and disaccharides can be found in both plants and animals.
Option d) is incorrect because both monosaccharides and disaccharides can be used for energy storage and
structural purposes, depending on their specific structure and function in the organism.
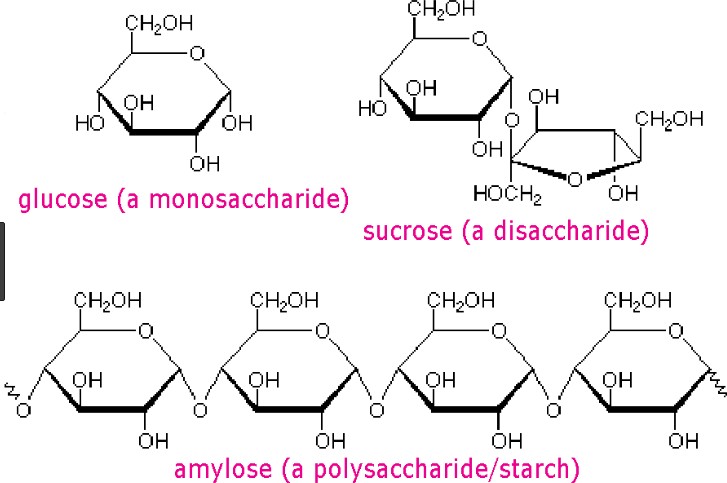 |
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
One of the key differences between skeletal muscles and cardiac muscles is the presence of intercalated discs in cardiac muscle tissue. These discs are specialized structures that facilitate communication and synchronization between cardiac muscle cells, allowing the heart to contract as a unified organ.
The other options are incorrect:
- A. Skeletal muscles are autorhythmic, whereas cardiac muscles are not: This is incorrect because cardiac muscles are autorhythmic; they can generate their own rhythmic contractions. Skeletal muscles require nervous system stimulation to contract.
- C. Skeletal muscles are found in the viscera, whereas cardiac muscles are found in the cranium: This is incorrect; skeletal muscles are primarily associated with the skeleton (attached to bones) and are not typically found in the viscera, while cardiac muscle is found in the heart.
- D. Cardiac muscles are voluntary, whereas skeletal muscles are involuntary: This is incorrect; skeletal muscles are voluntary (under conscious control), while cardiac muscles are involuntary (not under conscious control).
Therefore, the correct distinction is that cardiac muscles contain intercalated discs, while skeletal muscles do not.
This question was extracted from the actual TEAS Exam. Ace your TEAS exam with the actual TEAS 7 questions, Start your journey with us today
Visit Naxlex, the Most Trusted TEAS TEST Platform With Guaranteed Pass of 90%.
Money back guarantee if you use our service and fail the actual exam. Option of personalised live tutor on your area of weakness.
