The key structural difference between starch and cellulose is based on which of the following?
Starch fibrils have hydrogen bonds between fibrils, whereas cellulose fibrils do not.
Starch contains the aldohexose glucose, whereas cellulose contains the ketohexose fructose.
Starch contains alpha-glucose monomers, whereas cellulose contains beta-glucose monomers.
Starch strands have linear glucose monomers, whereas cellulose strands have cyclized glucose monomers.
Correct Answer : C
The key structural difference between starch and cellulose lies in the type of glucose monomers they contain:
- Starch is composed of alpha-glucose monomers, which are linked by α(1→4) glycosidic bonds.
- Cellulose is composed of beta-glucose monomers, which are linked by β(1→4) glycosidic bonds.
This difference in the orientation of the glucose molecules leads to different structural properties:
- In starch, the alpha-glucose linkage causes the molecules to form a helical, more easily digestible structure.
- In cellulose, the beta-glucose linkage results in straight, rigid chains that form strong fibers through hydrogen bonding, making it difficult for most organisms to digest.
The other options are incorrect:
- A. Incorrect, as cellulose fibrils do have hydrogen bonds, which contribute to its rigid structure.
- B. Incorrect, as both starch and cellulose are made of glucose, not fructose.
- D. Incorrect, both starch and cellulose contain cyclized glucose monomers, but the orientation differs.
TEAS 7 Exam Quiz Bank
HESI A2 Exam Quiz Bank
Find More Questions 📚
Teas 7 Questions: We got the latest updated TEAS 7 questions
100% Money Refund: 100% money back guarantee if you take our full
assessment pass with 80% and fail the actual exam.
Live Tutoring: Fully customized live tutoring lessons.
Guaranteed A Grade: All students who use our services pass with 90%
guarantee.
Related Questions
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
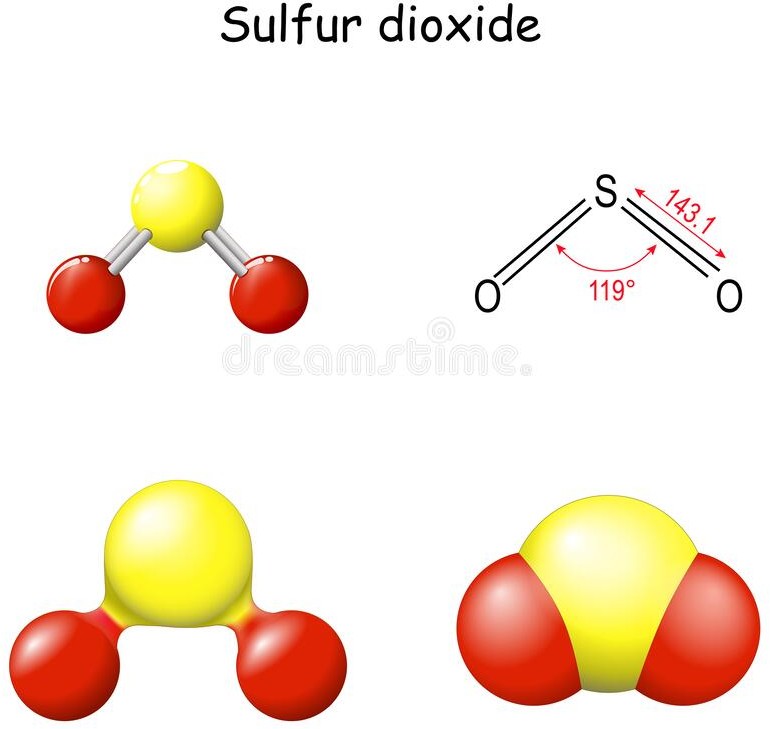
The molecular geometry of a molecule of sulphur dioxide (SO2) is bent or V-shaped. This is because of the presence of two lone pairs on the sulfur atom, which cause repulsion and distort the bond angles in the molecule.
SO2 has a central sulfur atom bonded to two oxygen atoms by double bonds. The two double bonds and the two lone pairs of electrons on sulfur result in a trigonal planar arrangement of electron pairs around the sulfur atom. However, the repulsion between the lone pairs causes the two oxygen atoms to be pulled closer together, resulting in a bent or V-shaped molecular geometry.
The bent molecular geometry of SO2 affects its properties, such as its polarity and reactivity. SO2 is a polar molecule due to the asymmetric distribution of electrons, which results in a partial positive charge on the sulfur atom and partial negative charges on the oxygen atoms. This polarity makes SO2 a good solvent and reactant in chemical reactions, as well as a contributor to air pollution and acid rain.
 |
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
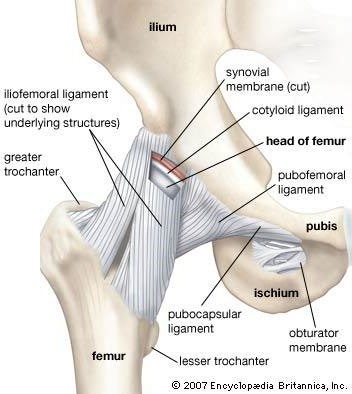
Ligaments are tough bands of fibrous tissue that connect two bones together in a joint. They provide stability and support to the joint, preventing excessive movement and helping to maintain proper alignment of the bones.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
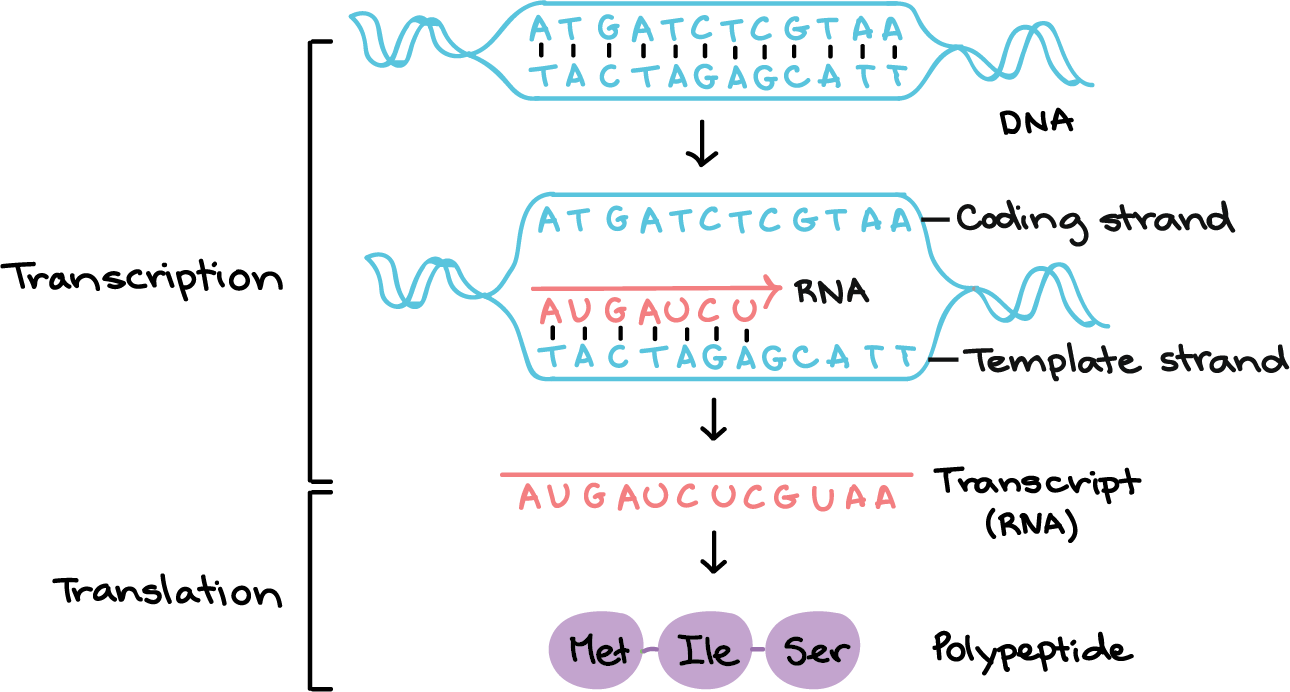
Transcription is the process by which DNA is copied into RNA. During transcription, the DNA molecule unwinds and RNA polymerase reads the DNA sequence and synthesizes a complementary RNA molecule using the DNA as a template.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
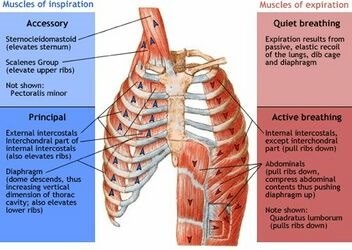
The diaphragm is a dome-shaped muscle that plays a key role in breathing. It separates the thoracic cavity, which contains the heart and lungs, from the abdominal cavity. When the diaphragm contracts, it moves downward and increases the volume of the thoracic cavity, allowing air to flow into the lungs. When it relaxes, it moves upward and decreases the volume of the thoracic cavity, forcing air out of the lungs.
 |
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
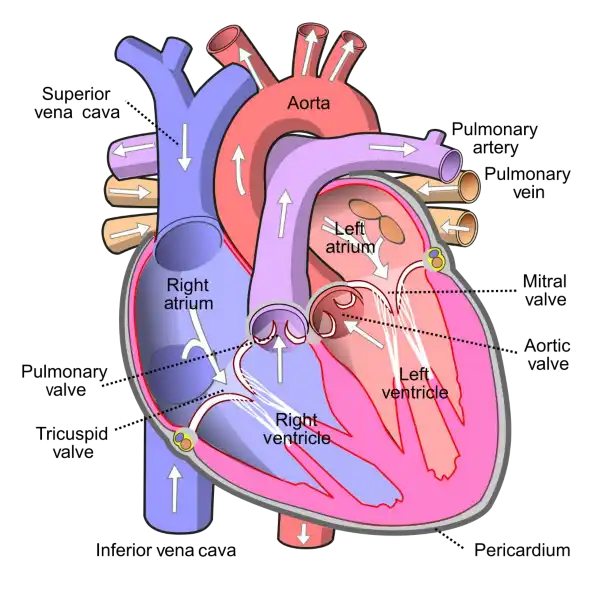
The mitral valve is located between the left atrium and left ventricle of the heart and helps to regulate the flow of blood between these chambers. It consists of two leaflets or flaps that open and close in response to changes in pressure as the heart beats.
During diastole, when the heart is relaxed and filling with blood, the mitral valve opens to allow blood to flow from the left atrium into the left ventricle. During systole, when the heart contracts to pump blood out of the left ventricle and into the systemic circulation, the mitral valve closes to prevent backflow of blood into the left atrium.
The mitral valve is one of four valves in the heart that help to ensure the unidirectional flow of blood through the heart and the rest of the circulatory system. Problems with the mitral valve, such as mitral valve prolapse or mitral stenosis, can lead to a range of symptoms and complications, including shortness of breath, fatigue, chest pain, and heart failure.
 |
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Electrons are subatomic particles that possess a very small mass compared to protons and neutrons. The mass of an electron is approximately 11836of the mass of a proton or neutron, making it negligible when calculating the atomic mass of an atom.
In atomic mass calculations, protons and neutrons are considered because they make up the bulk of the atom's mass:
- Proton: Positively charged, and each proton has a mass of about 1 atomic mass unit (amu).
- Neutron: Neutral charge, with a mass also close to 1 amu.
- Electron: Negligible mass, contributing very little to the atomic mass, which is why the atomic mass number is typically determined by the number of protons and neutrons.
Quarks are the fundamental constituents of protons and neutrons but are not typically referred to in terms of atomic mass.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
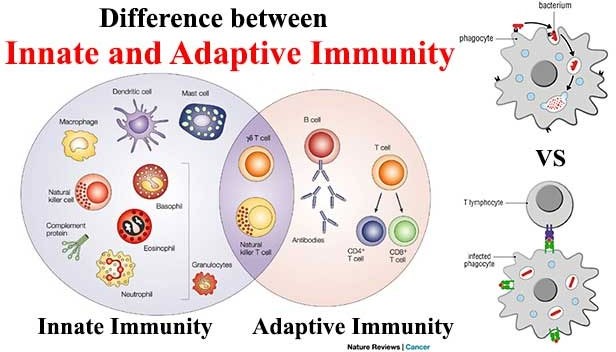
Innate immunity and adaptive immunity are two arms of the immune system that work together to protect the body from pathogens. Innate immunity is the first line of defense and is present at birth. It includes physical and chemical barriers such as the skin, mucous membranes, and antimicrobial peptides, as well as cells such as macrophages and natural killer cells that can quickly recognize and atack pathogens. Innate immunity is nonspecific, meaning it responds to a wide variety of pathogens in a similar way.
Adaptive immunity, on the other hand, is acquired after exposure to pathogens. It involves the production of antibodies and activation of T cells, which are specific to particular pathogens. Adaptive immunity takes longer to develop than innate immunity, but it provides a more specific and targeted response to pathogens. Once the adaptive immune system has been activated against a particular pathogen, it can provide long-term protection against future infections with that pathogen.
Option b) is incorrect because innate immunity is nonspecific while adaptive immunity is specific. Option c) is incorrect because antibodies are a part of adaptive immunity while T cells can be a part of both innate and adaptive immunity. Option d) is incorrect because adaptive immunity can provide long-term protection, while innate immunity provides immediate but short-lived protection.
 |
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
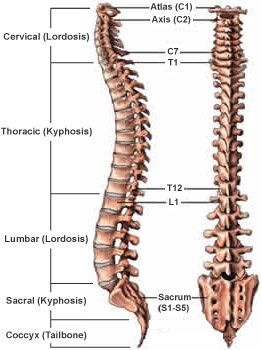
The vertebral column, also known as the spine or spinal column, is a series of bones called vertebrae that extend from the skull to the pelvis. It provides support for the body and protects the spinal cord. The five regions of the vertebral column, starting from the top and moving downwards, are:
- Cervical: This region is made up of seven vertebrae and is located in the neck. The first two cervical vertebrae, the atlas and the axis, are specialized to allow for head movement.
- Thoracic: This region is made up of twelve vertebrae and is located in the upper and middle back. The thoracic vertebrae are larger than the cervical vertebrae and articulate with the ribs.
- Lumbar: This region is made up of five vertebrae and is located in the lower back. The lumbar vertebrae are the largest and strongest of the vertebrae.
- Sacral: This region is made up of five fused vertebrae and is located in the pelvis. The sacrum forms the posterior wall of the pelvis and articulates with the hip bones.
- Coccygeal: This region is made up of four fused vertebrae and is located at the base of the vertebral column. The coccyx, or tailbone, provides atachment points for muscles and ligaments.
 |
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
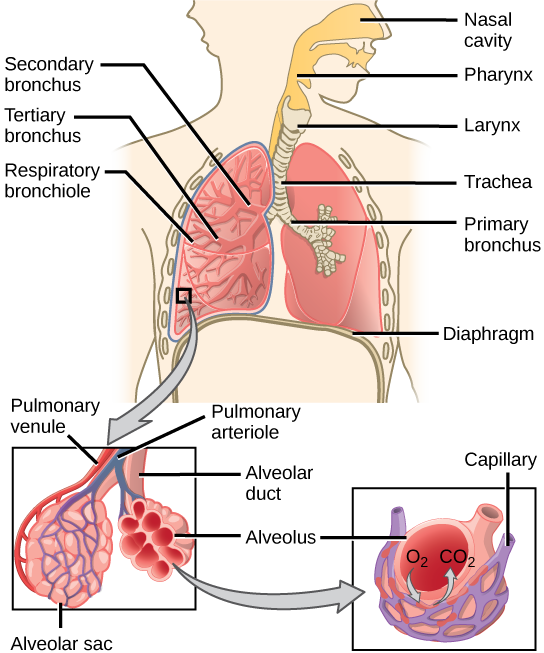
One of the main functions of the respiratory system is to facilitate the exchange of gases between the body and the environment. During inhalation, air enters the lungs and oxygen is absorbed into the bloodstream. During exhalation, carbon dioxide is removed from the body and expelled into the environment.
 |
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Chemical properties are characteristics of a substance that describe its ability to undergo a chemical change or reaction with another substance.
Reactivity with acid is a chemical property because it describes how a substance will react with an acid to produce a new substance. Density, melting point, and boiling point are physical properties that describe how a substance behaves under certain conditions but do not involve a chemical change or reaction.
This question was extracted from the actual TEAS Exam. Ace your TEAS exam with the actual TEAS 7 questions, Start your journey with us today
Visit Naxlex, the Most Trusted TEAS TEST Platform With Guaranteed Pass of 90%.
Money back guarantee if you use our service and fail the actual exam. Option of personalised live tutor on your area of weakness.
