A spoonful of sugar is added to a hot cup of tea. All the sugar dissolves. How can the resulting solution be described?
Saturated and homogeneous
Saturated and heterogeneous
Unsaturated and homogeneous
Unsaturated and heterogeneous
Correct Answer : C
Because more solute could be added and dissolve, the solution has not yet reached its limit and is considered unsaturated. Because all the solute dissolves, the particles in the mixture are evenly distributed as a homogenous mixture.
- A mixture is when elements and compounds are physically, but not chemically, combined.
- A homogeneous mixture is when substances mix evenly and it is impossible to see individual components. A heterogeneous mixture is when the substances mix unevenly and it is possible to see individual components.
- A solution is a type of homogeneous mixture that is formed when a solute dissolves in a solvent.
- The concentration of a solution is the amount of a substance in a given amount of solution. An unsaturated solution has the ability to dissolve more solute and a saturated solution has already reached the limit of solute it can dissolve.
TEAS 7 Exam Quiz Bank
HESI A2 Exam Quiz Bank
Find More Questions 📚
Teas 7 Questions: We got the latest updated TEAS 7 questions
100% Money Refund: 100% money back guarantee if you take our full
assessment pass with 80% and fail the actual exam.
Live Tutoring: Fully customized live tutoring lessons.
Guaranteed A Grade: All students who use our services pass with 90%
guarantee.
Related Questions
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Kidneys makes urine isincorrect.Kidneys do not make urine. They help regulate water balance, regulate levels of electrolytes such as sodium and potassium, and eliminate metabolic wastes. Urine is a byproduct of these functions.
As a person ages, kidney tissue and filtration capacity increase isincorrect. As a person ages, the kidneys and bladder change. This can affect functions such as bladder control and how well the kidneys filter blood. Kidney changes range from a decrease in kidney tissue to decreased filtration capacity.
Kidneys help regulate water balance iscorrect.Kidneys help regulate water balance, regulate levels of electrolytes such as sodium and potassium, and eliminate metabolic wastes. Urine is a byproduct of these functions.
Regulates levels of electrolytes such as sodium and potassium iscorrect.There must be a continual balance of water and salt in the blood. The urinary system, specifically the kidneys, help maintain this balance. It also balances levels of metabolites or electrolytes such as sodium, potassium, and calcium.
Eliminates metabolic wastes iscorrect. Urea, creatinine, uric acid, and ammonium are the primary types of nitrogenous wastes excreted from the body. The urinary system also detects and excretes excess water from the blood and out of the body.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Pathogenis an infectious foreign body that enters the body and causes disease or illness to the person. There are five types of pathogens: viruses, bacteria, fungi, protozoa, and worms. Pathogens have antigen proteins found on their surface and are unique to each pathogen.
Antibodyis a protein produced by the body’s immune system when it detects harmful substances (antigens). There are many different antibodies found in the body. Each one is unique and protects the body against the specific antigen that it detects at any given time. If there are no antibodies for a specific antigen, the more likely you are to develop an illness.
Vaccinationsare the introduction of a dead or disabled pathogen or of a harmless microbe with the protein of a pathogen on its surface into the body. Often administered through needle injection, to stimulate the immune system to produce immunity to a specific disease Immunity protects the body from a disease when exposed to it.
There are four types of immunity: natural/passive, natural/active, artificial/passive, and artificial/ active.
- Natural/passive – Babies receive immunities from breastmilk.
- Natural/active – The body produces antibodies to combat an illness when a person becomes sick.
- Artificial/passive – This immunity is temporary and requires doses of serum to maintain the immunity.
- Artificial/active – A vaccination provides artificial/active immunity.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
After scientists were able to view cells under the microscope they formulated the cell theory. One part of this theory concluded that all cells are alive. They also represent the basic unit of life.
All living things are made of cells. Cells are the smallest structural units and basic building blocks of living things. Cells contain everything necessary to keep living things alive. Varying in size and shape, cells carry out specialized functions. This theory, or in-depth explanation, about cells consists of three parts:
- All living things are composed of one or more cells.
- Cells are alive and represent the basic unit of life.
- All cells are produced from pre-existing cells.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
If the cohesion between particles decreases, then the particles must be undergoing a phase change that allows particles to move farther apart. This happens when a substance vaporizes and turns from liquid to gas. Any phase change that moves to the right in the diagram above requires energy to be added to the system because the substance has more energy at the end of the phase change. The phase changes aremelting,vaporization (boiling), andsublimation. When energy is added, particles move faster and can break away from each other more easily as they move to a state of matter with a higher amount of energy. This is most commonly done by heating the substance.
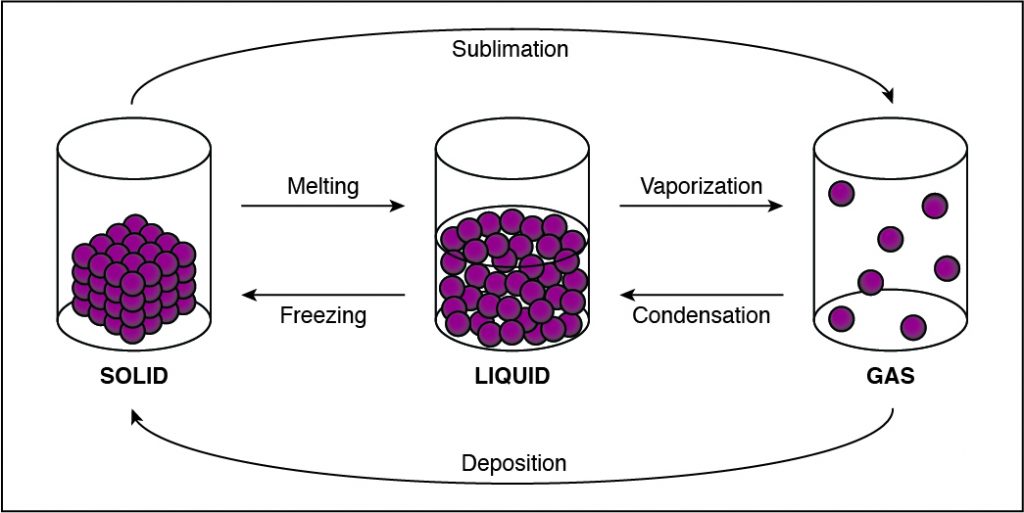
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
A neutralization reaction is a type of acid-base reaction where an acid and base react to form a salt and water.
In an aqueous solution, a base increases the hydroxide concentration (OH–), while an acid increases the hydrogen ion (H+) concentration. Sometimes,neutralization reactionsalso occur. This type of reaction happens when an acid and a base react with each other to form water and salt. Salt is typically defined as anionic compoundthat includes any cation except H+and any anion except OH–. Consider the following example of a neutralization reaction between hydrobromic acid (HBr) and potassium hydroxide (KOH).
HBr+KOH→KBr+H2O
Not all neutralization reactions proceed in the manner where all reactants are in the aqueous phase. In some chemical reactions, one reactant may be a solid. The neutralization reaction can still proceed to completion.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
The phenotype is the physical appearance of an organism, and the genotype is the set of alleles.
Mendel’s Theory of Heredity
To explain his results, Mendel proposed a theory that has become the foundation of the science of genetics. The theory has five elements:
- Parents do not transmit traits directly to their offspring. Rather, they pass on units of information calledgenes.
- For each trait, an individual has two factors: one from each parent. If the two factors have the same information, the individual ishomozygousfor that trait. If the two factors are different, the individual isheterozygousfor that trait. Each copy of a factor, orgene, is called anallele.
- The alleles determine the physical appearance, orphenotype. The set of alleles an individual has is itsgenotype.
- An individual receives one allele from each parent.
- The presence of an allele does not guarantee that the trait will be expressed
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
A control group is a factor that does not change during an experiment. Due to this, it is used as a standard for comparison with variables that do change such as a dependent variable.
Recall that these make up thescientific method,described below:
- Problem:The question created because of an observation.Example: Does the size of a plastic object affect how fast it naturally degrades in a lake?
- Research:Reliable information available about what is observed.Example: Learn how plastics are made and understand the properties of a lake.
- Hypothesis:A predicted solution to the question or problem.Example: If the plastic material is small, then it will degrade faster than a large particle.
- Experiment:A series of tests used to evaluate the hypothesis. Experiments consist of anindependent variablethat the researcher modifies and adependent variablethat changes due to the independent variable. They also include acontrol groupused as a standard to make comparisons.
- Example: Collect plastic particles both onshore and offshore of the lake over time. Determine the size of the particles and describe the lake conditions during this time period.
- Observe:Analyze data collected during an experiment to observe patterns.
- Example: Analyze the differences between the numbers of particles collected in terms of size.
- Conclusion:State whether the hypothesis is rejected or accepted and summarize all results.
- Communicate:Report findings so others can replicate and verify the results.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
The protein disc that holds two sister chromatids together is what collectively makes a chromosome. A gene is a segment of DNA, deoxyribonucleic acid, which transmits information from parent to offspring. A single molecule of DNA has thousands of genes. A chromosome is a rod-shaped structure that forms when a single DNA molecule and its associated proteins coil tightly before cell division.
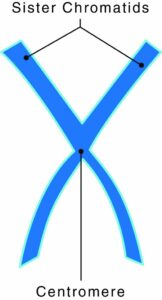
Chromosomes have two components:
- Chromatids: two copies of each chromosome
- Centromeres: protein discs that attach the chromatids together
Human cells have 23 sets of different chromosomes. The two copies of each chromosome are called homologous chromosomes, or homologues. An offspring receives one homologue from each parent. When a cell contains two homologues of each chromosome, it is termed diploid (2n). A haploid (n) cell contains only one homologue of each chromosome. The only haploid cells humans have are the sperm and eggs cells known as gametes.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Robert Hooke discovered the first cells in the mid-eighteenth century. The cell theory is a theory because it is supported by a significant number of experimental findings. The cell theory took many years to be developed because microscopes were not powerful enough to make such observations.
This theory, or in-depth explanation, about cells consists of three parts:
- All living things are composed of one or more cells.
- Cells are alive and represent the basic unit of life.
- All cells are produced from pre-existing cells.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
One step of the scientific method is to analyze information or data collected from the experiment to conclude whether the hypothesis is supported.
Recall that these make up thescientific method,described below:
- Problem:The question created because of an observation.Example: Does the size of a plastic object affect how fast it naturally degrades in a lake?
- Research:Reliable information available about what is observed.Example: Learn how plastics are made and understand the properties of a lake.
- Hypothesis:A predicted solution to the question or problem.Example: If the plastic material is small, then it will degrade faster than a large particle.
- Experiment:A series of tests used to evaluate the hypothesis. Experiments consist of anindependent variablethat the researcher modifies and adependent variablethat changes due to the independent variable. They also include acontrol groupused as a standard to make comparisons.
- Example: Collect plastic particles both onshore and offshore of the lake over time. Determine the size of the particles and describe the lake conditions during this time period.
- Observe:Analyze data collected during an experiment to observe patterns.
- Example: Analyze the differences between the numbers of particles collected in terms of size.
- Conclusion:State whether the hypothesis is rejected or accepted and summarize all results.
- Communicate:Report findings so others can replicate and verify the results.
This question was extracted from the actual TEAS Exam. Ace your TEAS exam with the actual TEAS 7 questions, Start your journey with us today
Visit Naxlex, the Most Trusted TEAS TEST Platform With Guaranteed Pass of 90%.
Money back guarantee if you use our service and fail the actual exam. Option of personalised live tutor on your area of weakness.
