During embryonic development, which of the following germ layers forms the nervous system?
Ectoderm
Endoderm
Mesoderm
Exoderm
Correct Answer : A
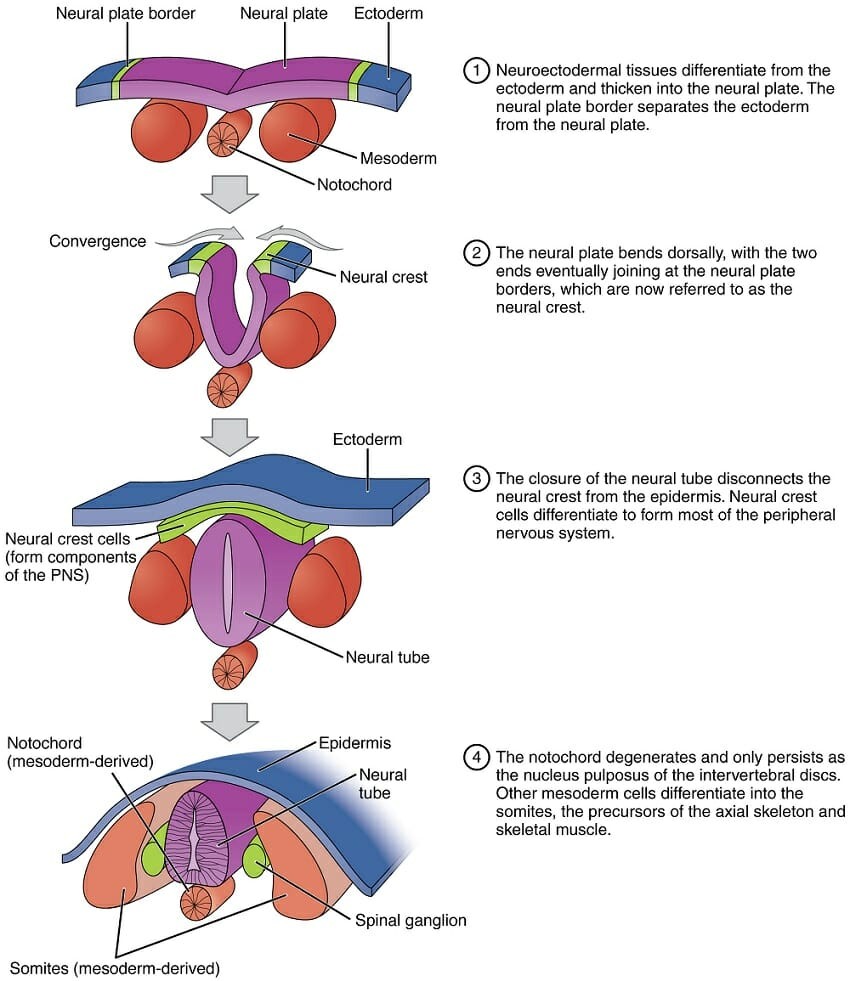
The three germ layers that form during embryonic development are the ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm. The ectoderm is the outermost layer, and it gives rise to the skin, hair, nails, and nervous system. The nervous system develops from a specialized region of the ectoderm called the neural plate, which invaginates to form the neural tube. The neural tube ultimately gives rise to the brain and spinal cord, which make up the central nervous system, as well as the peripheral nervous system. The endoderm gives rise to the lining of the digestive and respiratory tracts, while the mesoderm gives rise to the musculoskeletal system, circulatory system, and several other organs. The exoderm is not a germ layer and does not exist during embryonic development.
TEAS 7 Exam Quiz Bank
HESI A2 Exam Quiz Bank
Find More Questions 📚
Teas 7 Questions: We got the latest updated TEAS 7 questions
100% Money Refund: 100% money back guarantee if you take our full
assessment pass with 80% and fail the actual exam.
Live Tutoring: Fully customized live tutoring lessons.
Guaranteed A Grade: All students who use our services pass with 90%
guarantee.
Related Questions
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Spirometry is a common pulmonary function test that measures pulmonary ventilation, specifically assessing the volume and flow of air that can be inhaled and exhaled from the lungs. It provides important information about lung function and can help diagnose various respiratory conditions.
The other options do not relate to spirometry:
- A. Urinary capacity of the bladder: This is measured by urodynamics or bladder capacity tests, not spirometry.
- B. Volume of blood in the body: This can be estimated using different methods, such as dilution techniques or imaging, but not spirometry.
- D. Number of turns in the small intestine: This relates to the anatomy and function of the digestive system and is not measured by spirometry.
Thus, spirometry specifically evaluates how well the lungs are functioning in terms of air movement.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
The key structural difference between starch and cellulose lies in the type of glucose monomers they contain:
- Starch is composed of alpha-glucose monomers, which are linked by α(1→4) glycosidic bonds.
- Cellulose is composed of beta-glucose monomers, which are linked by β(1→4) glycosidic bonds.
This difference in the orientation of the glucose molecules leads to different structural properties:
- In starch, the alpha-glucose linkage causes the molecules to form a helical, more easily digestible structure.
- In cellulose, the beta-glucose linkage results in straight, rigid chains that form strong fibers through hydrogen bonding, making it difficult for most organisms to digest.
The other options are incorrect:
- A. Incorrect, as cellulose fibrils do have hydrogen bonds, which contribute to its rigid structure.
- B. Incorrect, as both starch and cellulose are made of glucose, not fructose.
- D. Incorrect, both starch and cellulose contain cyclized glucose monomers, but the orientation differs.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
A buffer is a solution that resists changes in pH when small amounts of an acid or base are added. Buffers work by neutralizing added hydrogen ions (H⁺) or hydroxide ions (OH⁻), thereby maintaining a relatively stable pH. Buffers are made up of a weak acid and its conjugate base or a weak base and its conjugate acid.
- A. It decreases the pH of the solution: This is incorrect because a buffer does not always decrease pH; it resists changes in both directions.
- C. It causes the pH of a solution to become neutral: Incorrect because buffers do not necessarily make a solution neutral; they stabilize pH around a certain value.
- D. It permanently binds hydrogen ions: Incorrect as the binding is reversible, which is essential for maintaining pH balance.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
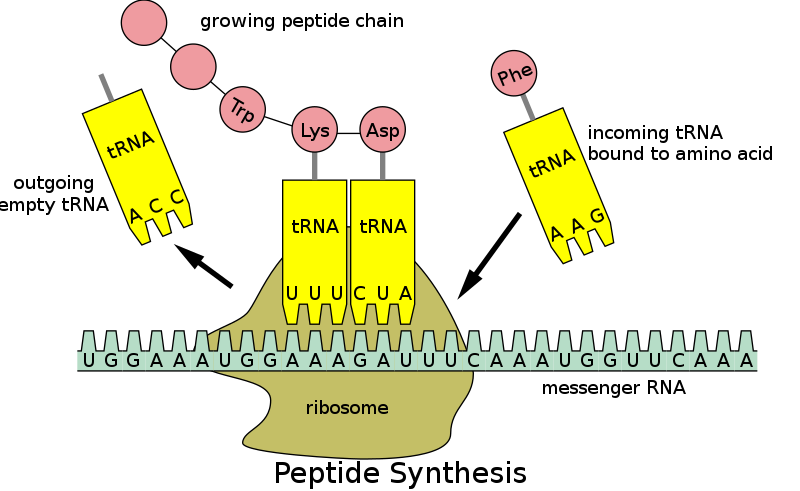
Transfer RNA (tRNA) is responsible for carrying amino acids to ribosomes during protein synthesis. Each tRNA molecule has a specific anticodon that matches a codon on the messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule. The tRNA molecule binds to the mRNA codon and brings the corresponding amino acid to the ribosome, where it is added to the growing polypeptide chain.
 |
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
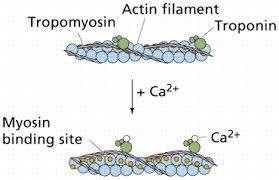
Muscle contraction is a complex process that involves the interaction between actin and myosin filaments in the muscle fibers. The sliding of these filaments is initiated by the release of calcium ions from the sarcoplasmic reticulum, a specialized organelle in muscle cells. The calcium ions bind to the protein troponin, which causes a conformational change in the troponin-tropomyosin complex, exposing the myosin-binding sites on actin. This allows the myosin heads to bind to actin, forming cross-bridges that pull the actin filaments towards the center of the sarcomere, resulting in muscle contraction.
Option a) is incorrect because calcium does not bind to tropomyosin directly, but rather binds to the protein troponin, causing a conformational change in the troponin-tropomyosin complex. Option c) is incorrect because calcium does not activate motor neurons, but rather is released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum in response to an action potential that travels down the motor neuron to the neuromuscular junction. Option d) is incorrect because calcium is required for muscle contraction, not relaxation. The relaxation of muscles after contraction is due to the active transport of calcium ions back into the sarcoplasmic reticulum, which allows the troponin-tropomyosin complex to return to its resting conformation, blocking the myosin-binding sites on actin and ending the cross-bridge cycle.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Stomach acid is highly acidic, primarily composed of hydrochloric acid (HCl), which means it has a low pH (around 1 to 3). Acids release hydrogen ions (H⁺) in solution, which lowers the pH.
- A. It has a higher pH: Incorrect, as acidic solutions have a lower pH compared to neutral distilled water (which has a pH of 7).
- B. It contains nitrogen: Incorrect, stomach acid is composed mostly of HCl, not nitrogen-containing compounds.
- D. It has more hydroxyl ions: Incorrect, acidic solutions have fewer hydroxyl ions (OH⁻); hydroxyl ions are more common in basic (alkaline) solutions.
In comparison to distilled water, which is neutral, the stomach acid solution has significantly more hydrogen ions, making it more acidic.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
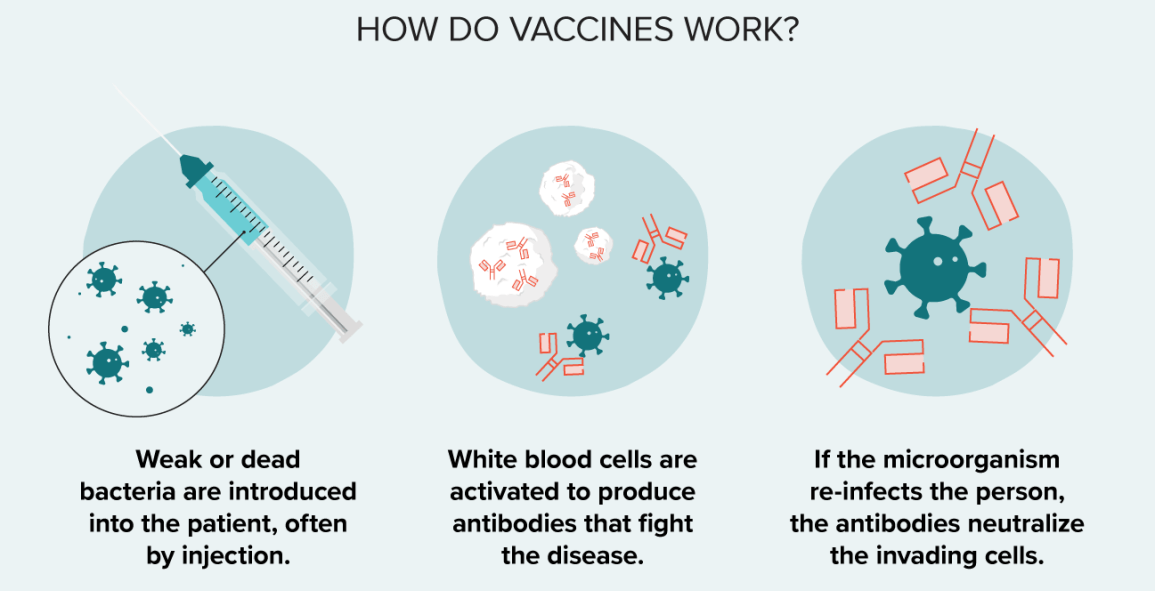
Vaccines are a type of preventative medicine that work by exposing the individual to a weakened or inactivated form of a pathogen (such as a virus or bacteria) or to a piece of the pathogen (such as a protein or sugar) that triggers an immune response in the body. This exposure allows the body to develop immunity to the pathogen without getting sick from the full-blown disease. Once the immune system has been primed, it can recognize and quickly respond to the pathogen if it is encountered again in the future, providing protection against the disease.
It is a common misconception that vaccines can cause the disease they are designed to protect against. This is not true. While some vaccines may cause mild symptoms such as a low-grade fever or soreness at the injection site, they do not cause the full-blown disease.
Vaccines provide active immunity, meaning that the body produces its own antibodies against the pathogen, rather than receiving pre-made antibodies as in passive immunity. Additionally, vaccines can be effective against both bacterial and viral infections, depending on the specific vaccine.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
The renal vein is responsible for draining oxygen-depleted blood from the kidneys and carrying it back to the heart through the inferior vena cava.
The other options refer to different structures:
- B. Renal Artery: Brings oxygenated blood to the kidneys, not draining it.
- C. Urethra: Transports urine from the bladder to the outside of the body, not involved in blood flow.
- D. Ureter: Carries urine from the kidneys to the bladder, also not related to blood drainage.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
One of the main functions of the respiratory system is to facilitate the exchange of gases between the body and the environment. During inhalation, air enters the lungs and oxygen is absorbed into the bloodstream. During exhalation, carbon dioxide is removed from the body and expelled into the environment.
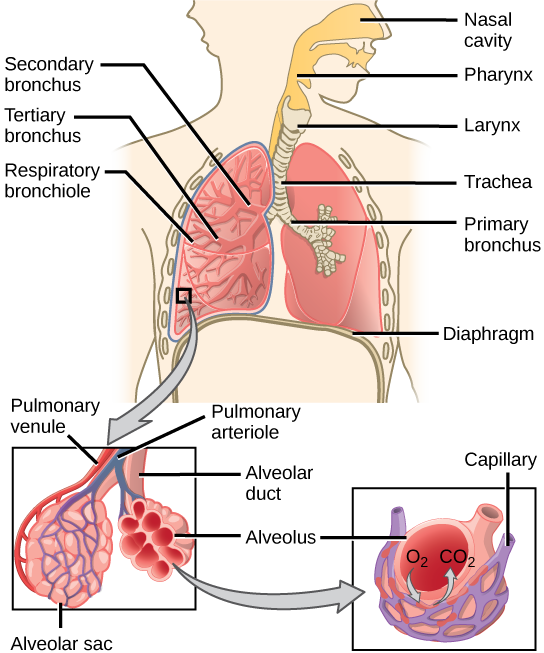 |
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Isotonic and isometric contractions are two types of muscle contractions that differ in the amount of force produced and the movement of the muscle. In isotonic contractions, the muscle changes length and produces movement, such as lifting a weight. The force generated by the muscle remains constant throughout the movement. Isotonic contractions can be further classified as concentric contractions, in which the muscle shortens as it contracts, and eccentric contractions, in which the muscle lengthens as it contracts.
In contrast, isometric contractions occur when the muscle generates force without changing its length or producing movement. For example, holding a weight in a fixed position without moving it requires an isometric contraction. In an isometric contraction, the force generated by the muscle increases up to a maximum and then remains constant. Isometric contractions can be used to build strength and endurance in the muscle, but they do not produce movement.
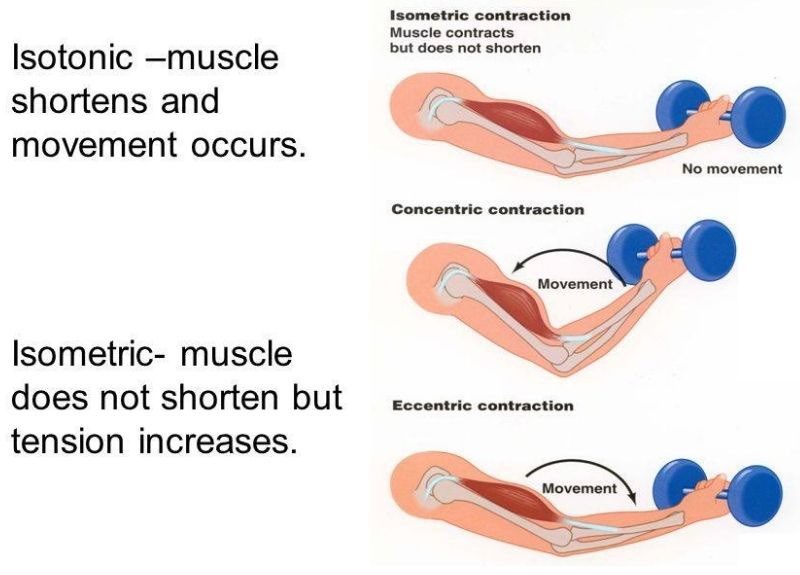 |
This question was extracted from the actual TEAS Exam. Ace your TEAS exam with the actual TEAS 7 questions, Start your journey with us today
Visit Naxlex, the Most Trusted TEAS TEST Platform With Guaranteed Pass of 90%.
Money back guarantee if you use our service and fail the actual exam. Option of personalised live tutor on your area of weakness.
