Blood oxygen levels are most likely low when blood _____.
leaves the aorta
fills the right atrium
reaches body tissues
flows through arteries
Correct Answer : B
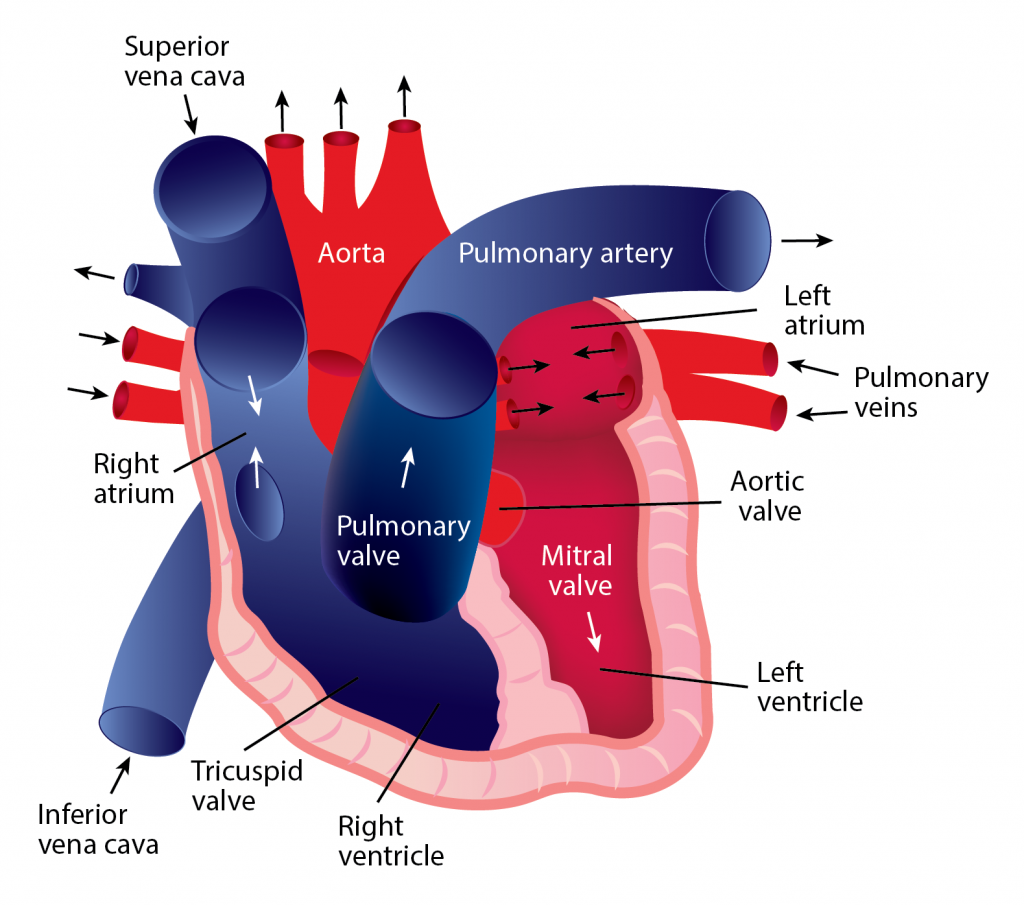
Blood continually flows in one direction, beginning in the heart and proceeding to the arteries, arterioles, and capillaries. When blood reaches the capillaries, exchanges occur between blood and tissues. After this exchange happens, blood is collected into venules, which feed into veins and eventually flow back to the heart’s atrium. The heart must relax between two heartbeats for blood circulation to begin.
Two types of circulatory processes occur in the body:
Systemic circulation
- The pulmonary vein pushes oxygenated blood into the left atrium.
- As the atrium relaxes, oxygenated blood drains into the left ventricle through the mitral valve. 3. The left ventricle pumps oxygenated blood to the aorta.
- Blood travels through the arteries and arterioles before reaching the capillaries that surround the tissues.
Pulmonary circulation
- Two major veins, the Superior Vena Cava and the Inferior Vena Cava, brings deoxygenated blood from the upper and lower half of the body.
- Deoxygenated blood is pooled into the right atrium and then sent into the right ventricle through the tricuspid valve, which prevents blood from flowing backward.
- The right ventricle contracts, causing the blood to be pushed through the pulmonary valve into the pulmonary artery.
- Deoxygenated blood becomes oxygenated in the lungs.
- Oxygenated blood returns from the lungs to the left atrium through the pulmonary veins.
TEAS 7 Exam Quiz Bank
HESI A2 Exam Quiz Bank
Find More Questions 📚
Teas 7 Questions: We got the latest updated TEAS 7 questions
100% Money Refund: 100% money back guarantee if you take our full
assessment pass with 80% and fail the actual exam.
Live Tutoring: Fully customized live tutoring lessons.
Guaranteed A Grade: All students who use our services pass with 90%
guarantee.
Related Questions
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Autotrophs are organisms that use basic raw materials in nature, like the sun, to make energy-rich biomolecules. Minerals are naturally inorganic.
Autotrophsare organisms that make energy-rich biomolecules from raw material in nature. They do this by using basic energy sources such the sun. This explains why most autotrophs rely on photosynthesis to transform sunlight into usable food that can produce energy necessary for life. Plants and certain species of bacteria are autotrophs.
Autotrophs, such as plants, use carbon dioxide (CO2) during photosynthesis to create chemical energy in the form of sugar molecules (like glucose) for growth.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
A neutralization reaction is a type of acid-base reaction where an acid and base react to form a salt and water.
In an aqueous solution, a base increases the hydroxide concentration (OH–), while an acid increases the hydrogen ion (H+) concentration. Sometimes,neutralization reactionsalso occur. This type of reaction happens when an acid and a base react with each other to form water and salt. Salt is typically defined as anionic compoundthat includes any cation except H+and any anion except OH–. Consider the following example of a neutralization reaction between hydrobromic acid (HBr) and potassium hydroxide (KOH).
HBr+KOH→KBr+H2O
Not all neutralization reactions proceed in the manner where all reactants are in the aqueous phase. In some chemical reactions, one reactant may be a solid. The neutralization reaction can still proceed to completion.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
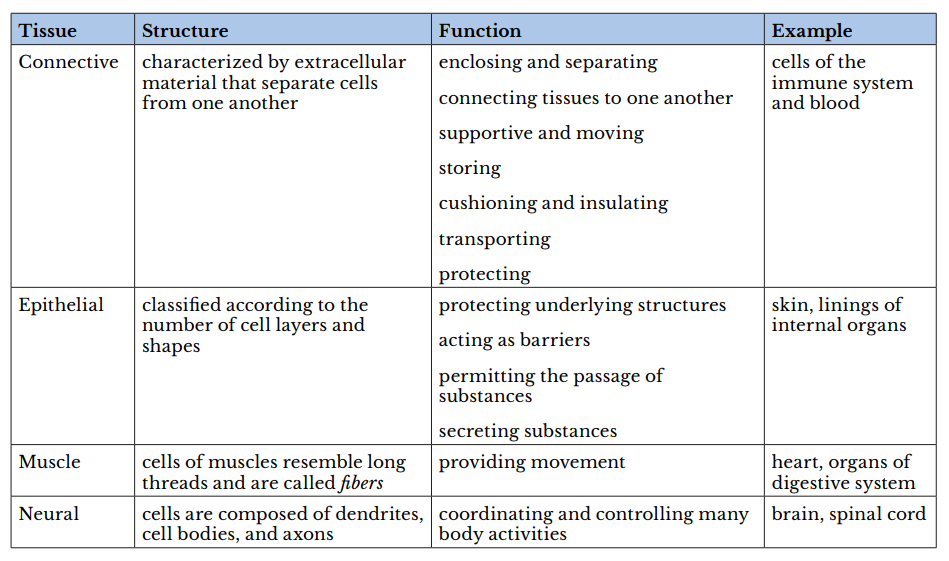
Atissueis a group of cells with similar structure and function and similar extracellular substances located between the cells. The table below describes the four primary tissues found in the human body.
body.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Because more solute could be added and dissolve, the solution has not yet reached its limit and is considered unsaturated. Because all the solute dissolves, the particles in the mixture are evenly distributed as a homogenous mixture.
- Amixtureis when elements and compounds are physically, but not chemically, combined.
- Ahomogeneousmixture is when substances mix evenly and it is impossible to see individual components. Aheterogeneousmixture is when the substances mix unevenly and it is possible to see individual components.
- Asolutionis a type of homogeneous mixture that is formed when a solute dissolves in a solvent.
- The concentration of a solution is the amount of a substance in a given amount of solution. Anunsaturatedsolution has the ability to dissolve more solute and asaturatedsolution has already reached the limit of solute it can dissolve.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Pathogenis an infectious foreign body that enters the body and causes disease or illness to the person. There are five types of pathogens: viruses, bacteria, fungi, protozoa, and worms. Pathogens have antigen proteins found on their surface and are unique to each pathogen.
Antibodyis a protein produced by the body’s immune system when it detects harmful substances (antigens). There are many different antibodies found in the body. Each one is unique and protects the body against the specific antigen that it detects at any given time. If there are no antibodies for a specific antigen, the more likely you are to develop an illness.
Vaccinationsare the introduction of a dead or disabled pathogen or of a harmless microbe with the protein of a pathogen on its surface into the body. Often administered through needle injection, to stimulate the immune system to produce immunity to a specific disease Immunity protects the body from a disease when exposed to it.
There are four types of immunity: natural/passive, natural/active, artificial/passive, and artificial/ active.
- Natural/passive – Babies receive immunities from breastmilk.
- Natural/active – The body produces antibodies to combat an illness when a person becomes sick.
- Artificial/passive – This immunity is temporary and requires doses of serum to maintain the immunity.
- Artificial/active – A vaccination provides artificial/active immunity.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Robert Hooke discovered the first cells in the mid-eighteenth century. The cell theory is a theory because it is supported by a significant number of experimental findings. The cell theory took many years to be developed because microscopes were not powerful enough to make such observations.
This theory, or in-depth explanation, about cells consists of three parts:
- All living things are composed of one or more cells.
- Cells are alive and represent the basic unit of life.
- All cells are produced from pre-existing cells.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Because this is a positive correlation, if the nutrient concentration increases or decreases, plant height will either increase or decrease accordingly.
While analyzing data, scientists tend to observe cause-and-effect relationships. These relationships can be quantified using correlations.Correlationsmeasure the amount of linear association between two variables. There are three types of correlations:
Positive correlation:
As one variable increases, the other variable also increases. This is also known as a direct correlation.
Negative correlation:
As one variable increases, the other decreases. The opposite is true if one variable decreases. A negative correlation is also known as an inverse correlation or an indirect correlation.
No correlation:
There is no connection or relationship between two variables.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
In this reaction, chlorine (Cl2) is an element in the reaction that replaces iodine in the compound sodium iodide (NaI). This allows chlorine to form a compound with sodium (NaCl) and leaves iodine (I2) as an element.
Synthesisreactions involve two or more reactants (A and B) combining to form one product (AB). In the example provided, hydrogen (H2) and oxygen (O2) begin as separate elements. At the end of the reaction, the hydrogen and oxygen atoms are bonded in a molecule of water (H2O).
Decompositionreactions have only one reactant (AB) that breaks apart into two or more products (A and B). In the example above, hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) breaks apart into two smaller molecules: water (H2O) and oxygen (O2).
Single-replacementreactions involve two reactants, one compound (AB) and one element (C). In this type of reaction, one element replaces another to form a new compound (AC), leaving one element by itself (B). In the example, zinc replaces hydrogen in hydrochloric acid (HCl). As a result, zinc forms a compound with chlorine, zinc chloride (ZnCl2), and hydrogen (H2) is left by itself.
Double-replacementreactions involve two reactants, both of which are compounds made of two components (AB and CD). In the example, silver nitrate, composed of silver (Ag1+) and nitrate (NO31-) ions, reacts with sodium chloride, composed of sodium (Na1+) and chloride (Cl1-) ions. The nitrate and chloride ions switch places to produce two compounds that are different from those in the reactants.
Combustionreactions occur when fuels burn, and they involve specific reactants and products, as seen in the examples below. Some form of fuel that contains carbon and hydrogen is required. Examples of such fuels are methane, propane in a gas grill, butane in a lighter, and octane in gasoline. Notice that these fuels all react with oxygen, which is necessary for anything to burn. In all combustion reactions, carbon dioxide, water, and energy are produced. When something burns, energy is released, which can be felt as heat and seen as light.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
The phenotype is the physical appearance of an organism, and the genotype is the set of alleles.
Mendel’s Theory of Heredity
To explain his results, Mendel proposed a theory that has become the foundation of the science of genetics. The theory has five elements:
- Parents do not transmit traits directly to their offspring. Rather, they pass on units of information calledgenes.
- For each trait, an individual has two factors: one from each parent. If the two factors have the same information, the individual ishomozygousfor that trait. If the two factors are different, the individual isheterozygousfor that trait. Each copy of a factor, orgene, is called anallele.
- The alleles determine the physical appearance, orphenotype. The set of alleles an individual has is itsgenotype.
- An individual receives one allele from each parent.
- The presence of an allele does not guarantee that the trait will be expressed
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
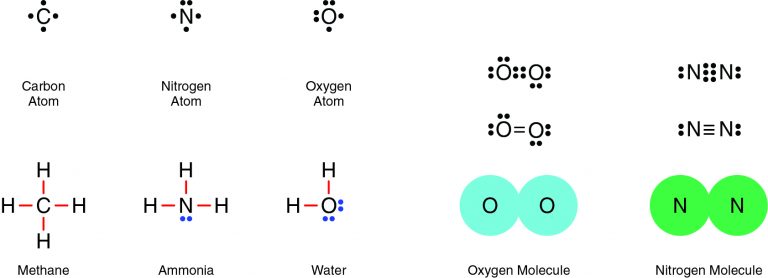
Nitrogen and oxygen are both nonmetals, which means they will share electrons in a covalent bond. For example, two oxygen atoms form a double bond, in which two pairs of electrons (four electrons total) are shared. Similarly, two nitrogen atoms form a molecule with a triple bond, in which three pairs of electrons (six electrons total) are shared.
This question was extracted from the actual TEAS Exam. Ace your TEAS exam with the actual TEAS 7 questions, Start your journey with us today
Visit Naxlex, the Most Trusted TEAS TEST Platform With Guaranteed Pass of 90%.
Money back guarantee if you use our service and fail the actual exam. Option of personalised live tutor on your area of weakness.
