Vital Signs Measurement
Temperature:
- Appropriate Sites for Measurement:
- Oral: Most common and suitable for cooperative children.
- Rectal: Most accurate but can be distressing for the child.
- Axillary: Least invasive but slightly less accurate.
- Tympanic: Quick and non-invasive, suitable for older children.
- Normal Pediatric Temperature Ranges Based on Age:
- Newborns: 97.7°F - 99.5°F (36.5°C - 37.5°C)
- Infants: 97.7°F - 99.5°F (36.5°C - 37.5°C)
- Toddlers/Preschoolers: 97.7°F - 99.5°F (36.5°C - 37.5°C)
- School-Age Children: 97.7°F - 99.5°F (36.5°C - 37.5°C)
- Adolescents: 97.0°F - 99.0°F (36.1°C - 37.2°C)
- Recognizing Signs of Fever and Hypothermia:
- Fever: Elevated body temperature, flushed skin, sweating, irritability.
- Hypothermia: Low body temperature, shivering, lethargy, pallor.
Heart Rate:
- Normal Pediatric Heart Rate Ranges Based on Age:
- Newborns: 120 - 160 bpm
- Infants (1-12 months): 80 - 140 bpm
- Toddlers (1-3 years): 80 - 130 bpm
- Preschoolers (3-6 years): 75 - 120 bpm
- School-Age Children (6-12 years): 70 - 110 bpm
- Adolescents (12-18 years): 60 - 100 bpm
- Assessing Heart Rate Rhythm and Regularity:
- Palpate pulse for strength, and regularity, note any irregularities (e.g., arrhythmias) and delays.
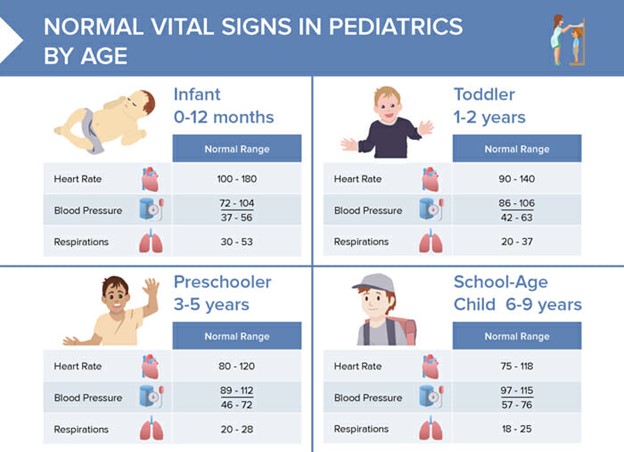
Respiratory Rate:
- Normal Pediatric Respiratory Rate Ranges Based on Age:
- Newborns: 30 - 60 breaths per minute
- Infants (1-12 months): 24 - 38 breaths per minute
- Toddlers (1-3 years): 22 - 34 breaths per minute
- Preschoolers (3-6 years): 20 - 30 breaths per minute
- School-Age Children (6-12 years): 18 - 26 breaths per minute
- Adolescents (12-18 years): 12 - 22 breaths per minute
- Assessing Respiratory Effort and Quality:
- Observe chest movement, use of accessory muscles,
- Signs of distress:
- Shortness of breath.
- Fast breathing, or taking lots of rapid, shallow breaths.
- Fast heart rate.
- Coughing produces phlegm.
- Blue fingernails or blue tone to the skin or lips.
- Extreme tiredness.
- Fever.
- Crackling sound in the lungs.
Blood Pressure:
- Determining Appropriate Cuff Size:
- Cuff width should cover 40% of the upper arm circumference.
- Normal Pediatric Blood Pressure Ranges Based on Age:
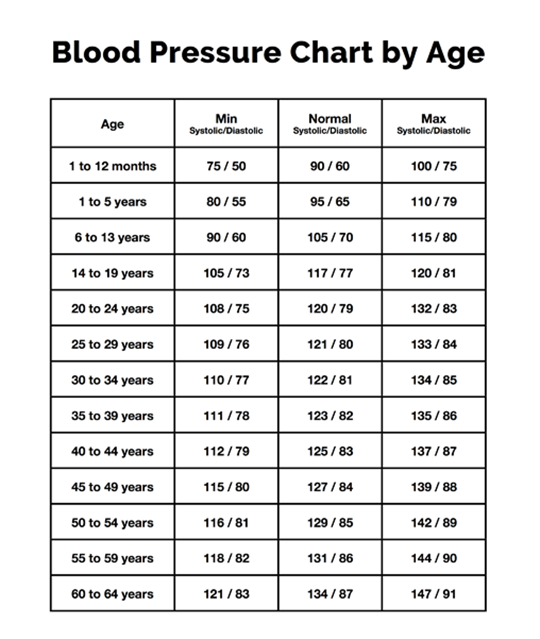 - Signs of Hypertension and Hypotension:
- Signs of Hypertension and Hypotension:
- Hypertension: Elevated blood pressure, headache, nosebleeds.
- Hypotension: Low blood pressure, dizziness, pallor, weakness.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Questions on Vital Signs Measurement
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Search Here
Related Topics
- Stages of physical, cognitive, social and emotional development from infancy to adolescence - Pediatric Nursing Skills and Pediatric Assessment
- Developmental milestones and screening tools - Pediatric Nursing Skills and Pediatric Assessment
- Factors affecting growth and development - Pediatric Nursing Skills and Pediatric Assessment
- Interventions to promote optimal development - Pediatric Nursing Skills and Pediatric Assessment
- Conclusion - Pediatric Nursing Skills and Pediatric Assessment
More on Nursing
Free Nursing Study Materials
Access to all study guides and practice questions for nursing for free.
- Free Nursing Study Trials
- Free Nursing Video tutorials
- Free Nursing Practice Tests
- Free Exam and Study Modes
- Free Nursing Revision Quizlets
