What is the advantage of teaching to the family about continuous cycling peritoneal dialysis (CCPD) or continuous ambulatory peritoneal (CAPD) for adolescents who require dialysis?
Hospitalization is only required several nights per week
Adolescents can carry out procedures themselves
Dietary restrictions are no longer necessary
Insertion of a catheter does not require surgical placement
The Correct Answer is B
One of the advantages of CCPD and CAPD is that they allow for more flexibility and independence in performing peritoneal dialysis treatments, especially for older children and adolescents. With proper training and supervision, adolescents can learn to carry out many aspects of the dialysis procedure themselves, which can provide them with a greater sense of control and autonomy over their healthcare.
The other options are not accurate advantages of CCPD or CAPD:
A. Hospitalization is only required several nights per week: CCPD and CAPD are typically performed at home, and hospitalization is not required for routine treatments. However, regular clinic visits and follow-ups are still necessary.
C. Dietary restrictions are no longer necessary: Dietary restrictions may still be necessary for patients on peritoneal dialysis to manage their fluid and electrolyte balance. The extent of dietary restrictions can vary depending on the individual patient's needs.
D. Insertion of a catheter does not require surgical placement: The insertion of a peritoneal dialysis catheter does require a surgical procedure. The advantage of CCPD and CAPD is more related to the flexibility and independence of performing dialysis at home rather than the method of catheter insertion.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Obstructive congenital heart defects involve the presence of narrowing or constriction in various parts of the heart or major blood vessels. In the case of coarctation of the aorta, there is a narrowing or constriction in the aorta, which can obstruct blood flow. Aortic stenosis involves the narrowing of the aortic valve, and pulmonic stenosis involves the narrowing of the pulmonary valve. These defects create obstacles to the normal flow of blood out of the heart, leading to increased pressure within the heart and affecting blood circulation.
The other categories mentioned are:
B. Mixing defects: These defects involve abnormal mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood within the heart, typically due to septal defects like atrial septal defect (ASD) or ventricular septal defect (VSD).
C. Decreased pulmonary blood flow: These defects are characterized by reduced blood flow to the lungs, such as in the tetralogy of Fallot.
D. Increased pulmonary blood flow: These defects involve increased blood flow to the lungs, often due to shunting of blood from the left side of the heart to the right side, as seen in atrial septal defects or ventricular septal defects.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
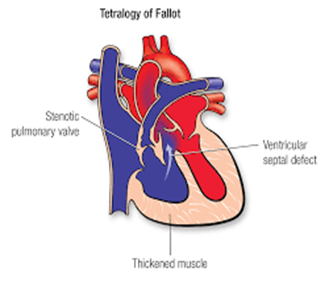
Tetralogy of Fallot is a congenital heart defect characterized by four specific abnormalities:
Ventricular septal defect (VSD): This is a hole in the wall (septum) between the two lower chambers (ventricles) of the heart.
Overriding aorta: The aorta is positioned over both the left and right ventricles, which allows oxygen-poor (deoxygenated) blood from the right ventricle to be pumped into the aorta and to the body.
Pulmonic stenosis (PS): This is a narrowing of the pulmonary valve or artery that restricts blood flow from the right ventricle to the lungs.
Right ventricular hypertrophy: The right ventricle becomes thicker and more muscular as it works harder to pump blood against the narrowed pulmonary valve or artery.
Options A, C, and D describe different congenital heart conditions and defects, but they are not associated with Tetralogy of Fallot:
A. Coarctation of aorta, aortic valve stenosis, mitral valve stenosis, and patent ductus arteriosus are not part of the constellation of defects seen in the Tetralogy of Fallot.
C. Describing the aorta exiting from the right ventricle and pulmonary artery exiting from the left ventricle with two noncommunicating circulations is characteristic of transposition of the great arteries, not Tetralogy of Fallot.
D. Tricuspid valve atresia, atrial septal defect, ventricular septal defect, and hypoplastic right ventricle describe a different congenital heart condition, not Tetralogy of Fallot.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
