The nurse is caring for a 5-week-old infant who has been experiencing projectile vomiting after feedings. What additional symptom should the nurse anticipate?
Stool containing mucus and blood.
An olive-sized mass in the epigastric region.
Frequent burping accompanied by poor feeding.
Rebound tenderness in the left lower abdominal quadrant.
The Correct Answer is B
Choice A rationale
While it’s possible for an infant with projectile vomiting to have stool containing mucus and blood, this is not typically associated with the condition that most commonly causes projectile vomiting in infants, which is pyloric stenosis.
Choice B rationale
An olive-sized mass in the epigastric region is a classic symptom of pyloric stenosis. This condition occurs when the muscle between the stomach and the small intestine (the pylorus) thickens, preventing food from moving from the stomach to the intestine.
Choice C rationale
Frequent burping and poor feeding can be symptoms of many different conditions in infants, but they are not typically associated with pyloric stenosis.
Choice D rationale
Rebound tenderness in the left lower abdominal quadrant is a symptom of conditions like appendicitis, but it is not typically associated with pyloric stenosis.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Choice A rationale
Diaphragmatic respirations are not typically associated with acute respiratory distress in a child with respiratory syncytial virus (RSV). Diaphragmatic respirations are normal in infants and young children.
Choice B rationale
A resting respiratory rate of 35 breaths/min is within the normal range for a 1-year-old child and would not typically indicate acute respiratory distress.
Choice C rationale
Bilateral bronchial breath sounds are normal findings and would not typically indicate acute respiratory distress in a child with RSV45.
Choice D rationale
Flaring of the nares, or nostrils, can be a sign of respiratory distress in infants and young children. It indicates that the child is using additional muscles to breathe, which can occur when the lower airways are blocked or narrowed, as in a severe RSV infection.
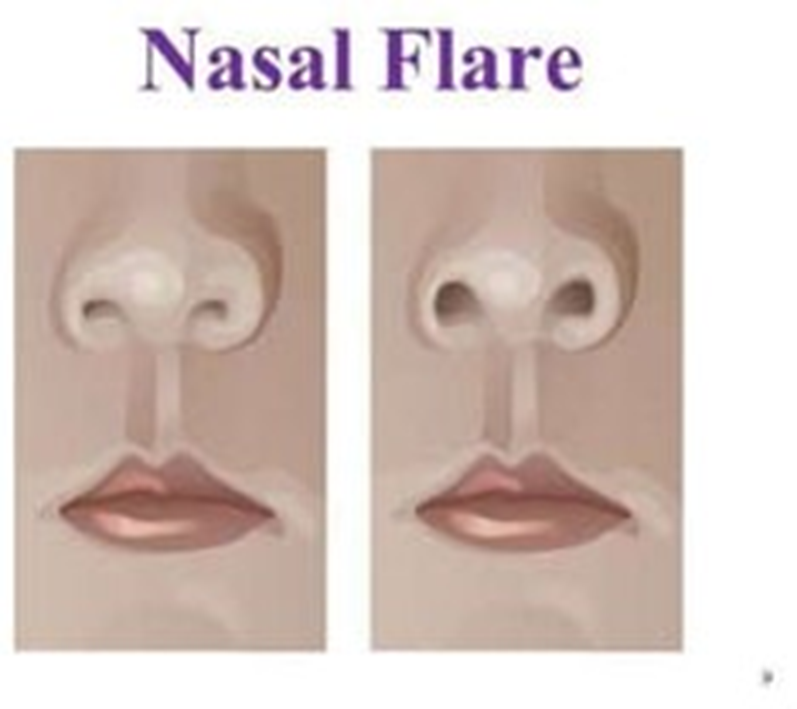
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Choice A rationale
Dividing the gluteal area into quarters and giving the IM injection into the upper outer quadrant is not the recommended technique for a 16-month-old toddler. This site is not typically used until after the child has begun walking regularly and has developed sufficient muscle mass.
Choice B rationale
Administering the injection into the middle of the lateral aspect of the thigh is the recommended technique for a 16-month-old toddler. The vastus lateralis muscle in the thigh is usually the preferred site for IM injections in infants and young children.
Choice C rationale
Using a needle length of 1/2 inch (1.25 cm) to avoid deep tissue damage is not the recommended technique for a 16-month-old toddler. The needle length should be appropriate for the age and size of the child, and a 1/2 inch needle may not be long enough to reach the muscle tissue.
Choice D rationale
Giving the injection in the arm, one to 2 inches (2.5 to 5.0 cm) below the acromion process, is not the recommended technique for a 16-month-old toddler. The deltoid muscle in the arm is typically not used for IM injections until after the child is 3 years old.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
