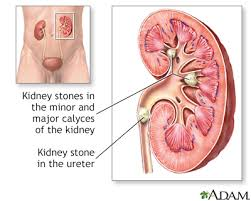
The client has passed a renal calculus that is determined to be composed of calcium oxalate. Which discharge instruction should be given by the nurse?
Increase sodium intake.
Consider a move to an area with higher humidity.
Increase water intake.
Decrease intake of all calcium-rich foods and beverages.
The Correct Answer is C
Choice A Reason
Increasing sodium intake is not recommended for patients who have passed a calcium oxalate stone. High sodium intake can increase calcium in the urine, which can contribute to the formation of new stones. Therefore, patients are often advised to limit their sodium intake to reduce the risk of stone recurrence.
Choice B Reason
Considering a move to an area with higher humidity is not a standard recommendation for preventing the recurrence of calcium oxalate stones. While climate can affect hydration levels, it is more important for the patient to focus on direct measures to stay hydrated, such as drinking more fluids.
Choice C Reason
Increasing water intake is a key recommendation for patients who have had calcium oxalate stones. Adequate hydration is essential to dilute the urine, which helps prevent the formation of new stones. Patients are often advised to drink enough water to produce at least 2.5 liters of urine per day.
Choice D Reason
Decreasing the intake of all calcium-rich foods and beverages is not generally recommended for patients with calcium oxalate stones. In fact, a moderate intake of dietary calcium can help reduce the risk of stone formation by binding with oxalate in the intestines, which prevents it from being absorbed into the urine. Patients should consult with a healthcare provider or dietitian to determine the appropriate amount of dietary calcium.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is ["B","D"]
Explanation
Choice A reason:
Cyanosis, or a bluish discoloration of the skin, particularly in the nail beds, is a sign of inadequate oxygenation and would not indicate successful intervention. The absence of cyanosis would be a positive outcome, reflecting improved oxygen saturation.
Choice B reason:
Lungs clear to auscultation would indicate that air is moving through all regions of the lungs without obstruction from fluid or mucus, which is a sign of recovery from pneumonia. This finding suggests that the interventions aimed at improving gas exchange, such as positioning, deep breathing exercises, and suctioning if needed, have been effective.
Choice C reason: The inability to speak in full sentences often indicates respiratory distress and would not be a sign of successful nursing intervention. An improvement would be the client's ability to speak in full sentences without difficulty, reflecting better lung function and gas exchange.
Choice D reason:
Pulse oximetry readings between 94-96% on room air are within normal limits and indicate adequate oxygen saturation and gas exchange. This is a clear sign that the client's respiratory status has improved, and the interventions for Impaired Gas Exchange have been successful.
Choice E reason:
Bronchovesicular breath sounds are normal breath sounds heard over the major bronchi and are typically moderate in pitch and intensity. However, they are not specifically indicative of successful intervention for Impaired Gas Exchange. The absence of abnormal sounds such as crackles or wheezes would be more relevant.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Choice A Reason
Metoprolol, a beta-blocker, can cause fluid retention, which may lead to swelling in the ankles. However, this is not a common side effect and is not typically included as a standard warning for patients starting on metoprolol. Patients should be aware of this potential side effect but also understand that it may not occur.
Choice B Reason
Patients should not stop taking metoprolol abruptly, especially if they experience fatigue, which can be a common side effect. Abrupt cessation can lead to rebound hypertension or angina. Instead, patients should consult their healthcare provider if they experience significant fatigue that impacts their daily activities.
Choice C Reason
Checking the pulse is an important self-monitoring measure for patients on metoprolol. This medication can slow the heart rate, and patients should be instructed on how to check their pulse and what to do if it falls below a certain rate, as advised by their healthcare provider.
Choice D Reason
While staying hydrated is generally good advice, there is no specific need to drink plenty of fluids related to the use of metoprolol for angina pectoris. Patients should follow normal hydration guidelines unless otherwise directed by their healthcare provider.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
