The ultimate challenge nursing students must conquer in preparation for laying the foundation of their medical profession is the NCLEX exam. This extensive exam assesses the competencies necessary for safe and efficient nursing practice. The gastrointestinal (GI) system is one of the major content areas covered in the exam. Here's a thorough look at how nursing students can become experts in GI-related material to ace the NCLEX. Thus, explore GI NCLEX questions.
How can Naxlex help?
Naxlex is the ultimate nursing resource for students. We will be at your disposal to help you master your GI NCLEX with our personalized practice exams and live tutoring for areas of weakness to warrant your success. We guarantee a pass rate of 90%, with a money-back offer if you score 85% in our assessments and fail the actual exam. Try our premium package today!
Nursing Test Banks
Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Comprehending the NCLEX Exam
The NCLEX exam consists of multiple-choice questions and other question types in alternate formats, such as ordered answer and select-all-that-apply, otherwise referred to as SATA. The NCLEX is adaptive, meaning the questions' difficulty level changes according to the test-taker's performance. Consequently, a firm lay hold of GI principles is significant because the questions that cover this subject might be simple or complicated, and it is essential to be well prepared. Critical thinking is a necessary skill, as is proper time management. Students can become more comfortable with the structure and subject matter of the exam by regularly practicing questions related to the GI NCLEX.
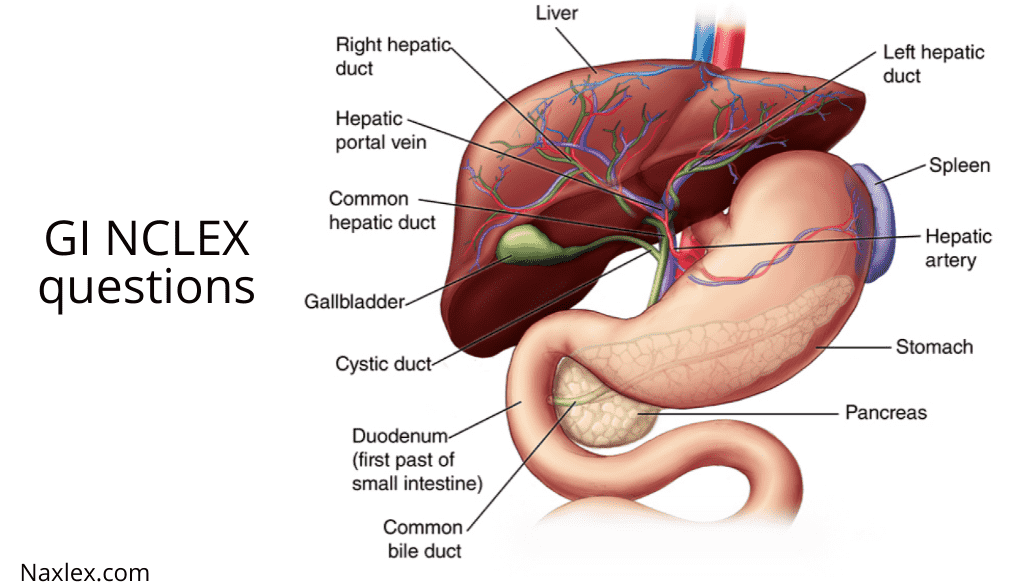
Anatomy and Physiology of the GI System
Nursing students must first make sense of the anatomy and physiology of the gastrointestinal tract to be aware of GI problems and how to remedy them. This entails being familiar with the organs and structures associated with digestion, including the liver, gallbladder, pancreas, small and large intestines, stomach, esophagus, and mouth. Comprehending the ingestion, digestion, absorption, and excretion processes is essential. For example, understanding GI physiology requires understanding the role of bile in emulsifying lipids and the role of enzymes in breaking down nutrients.
Common GI illnesses
Nursing students are required to understand the pathophysiology, clinical presentation, and treatment of common GI illnesses. These might comprise the following:
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a digestive disease in which bile or stomach acid inflames the lining of the food pipe. Its symptoms include regurgitation and heartburn caused by the reflux of stomach contents into the esophagus.
Gastric or duodenal mucosa erosion due to Helicobacter pylori infection or NSAID use is known as peptic ulcer disease.
The expression "inflammatory bowel disease" (IBD) refers to a group of gastrointestinal disorders that are chronic and characterized by flare-ups and remissions. These disorders include Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis.
Stomach pain, bloating, and altered bowel habits without signs of an organic disease are the hallmarks related to irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), a common disorder of the gastrointestinal tract.
Gallstones are solid particles in the bile ducts or gallbladder and can cause choledocholithiasis or cholecystitis.
Diagnostic Procedures and Laboratory Tests
Nursing students must comprehend the purpose, logistics, and implications of diagnostic tests frequently employed to assess gastrointestinal problems. These could consist of:
Endoscopy and colonoscopy: invasive methods for GI tract visualization and tissue sample collection for biopsies.
Barium swallow and upper GI series: radiographic examinations evaluating the anatomy and purpose of the esophagus, stomach, and upper small intestine.
Imaging studies: To check for structural malformations or consequences of GI illnesses, imaging procedures like computed tomography, otherwise known as CT, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and ultrasound may be used.
Laboratory tests: amylase, lipase, liver function tests (LFTs), stool studies, complete blood counts (CBCs), and lipase tests can all offer important diagnostic insights.
Pharmacological Interventions
Students studying nursing should be knowledgeable about the medications used to treat gastrointestinal diseases, such as:
Drugs that regulate stomach acid output include proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) and histamine-2 receptor antagonists, or H2 blockers, which treat peptic ulcer disease and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
Antidiarrheal and laxative agents: medications that help treat constipation and diarrhea include psyllium and loperamide.
Antiemetics: Medication used to treat gastrointestinal problems that cause nausea and vomiting includes promethazine and ondansetron.
Antibiotics: Doctors may use medications, including metronidazole and clarithromycin, for the treatment of bacterial infections like H.pylori in peptic ulcer disease.
Nursing Management of Gastrointestinal Illnesses
A comprehensive strategy that includes assessment, diagnosis, planning, execution, and evaluation is used in nursing care for patients with GI illnesses. Among the nursing interventions are:
Evaluation: Thoroughly examines the patient's gastrointestinal symptoms, nutritional state, medical history, and psychological aspects.
Nursing diagnosis is based on identifying issues such as impaired skin integrity, danger of aspiration, or imbalanced nutrition.
Planning: To treat GI symptoms, encourage an ideal diet, and avoid problems, collaborative goal-setting with the patient and interdisciplinary team is necessary.
Implementation: Giving patients information about their health and treatment plan, monitoring for side effects, giving nutritional counseling, and administering medication are examples of nurse interventions.
Evaluation: Continuous monitoring of the patient's reaction to therapies, adjustment of the care plan as necessary, and outcome assessment
Conclusion: GI NCLEX Questions
Understanding the GI system is crucial for nursing students preparing for the NCLEX exam because the test contains numerous questions about GI illnesses. Students can become more prepared and confident when answering NCLEX questions by learning about anatomy, physiology, joint disorders, diagnostic techniques, pharmaceutical therapies, and GI system nursing management strategies. Through perseverance, analytical thinking, and a firm grasp of GI principles, nursing students can successfully negotiate the intricacies of the examination and begin their path to becoming qualified and sympathetic registered nurses.
Start your journey with us today
Join 1000+ Nursing Students
Powerful learning and clinical tools combined into one platform. The Naxlex Knowledge and Qbanks give you instant and on-the-go nursing knowledge and guidance.




